Figure 3.
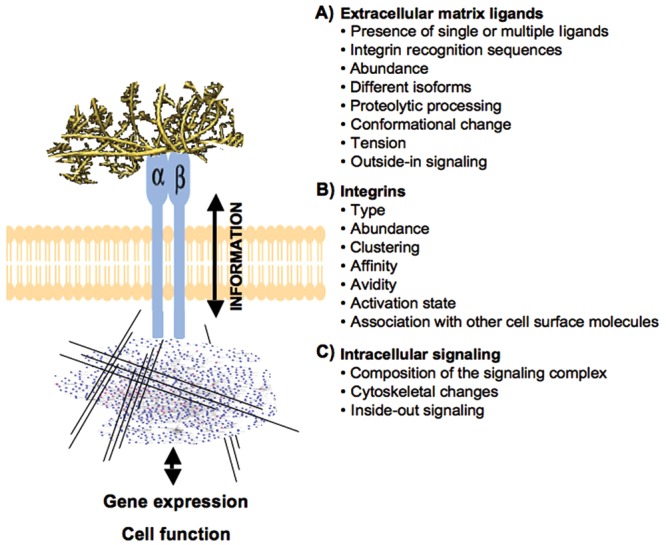
Summary of the key factors regulating integrin-mediated interactions and information exchange between the cell and extracellular matrix (ECM). Integrins mediate cell adhesion and migration on the ECM and function as two-way mediators of information between the ECM and cells. (A) While attaching the cells to the pericellular matrix, integrins also sense changes in the properties (e.g., tension, proteolytic processing, conformational change) and composition of the ECM and relay this information outside-in to the cell. (B) The information exchange through integrins is modulated by and depends on several integrin-related factors, including integrin type, abundance, clustering, etc. (C) Interaction with the matrix triggers distinct signaling cascades and cytoskeletal changes allowing the cell to adapt its functions appropriately. Reciprocally, changes in the function of intracellular signaling networks or cytoskeleton modulate integrin activity that can then lead to appropriate changes in the cells’ interactions with the ECM.
