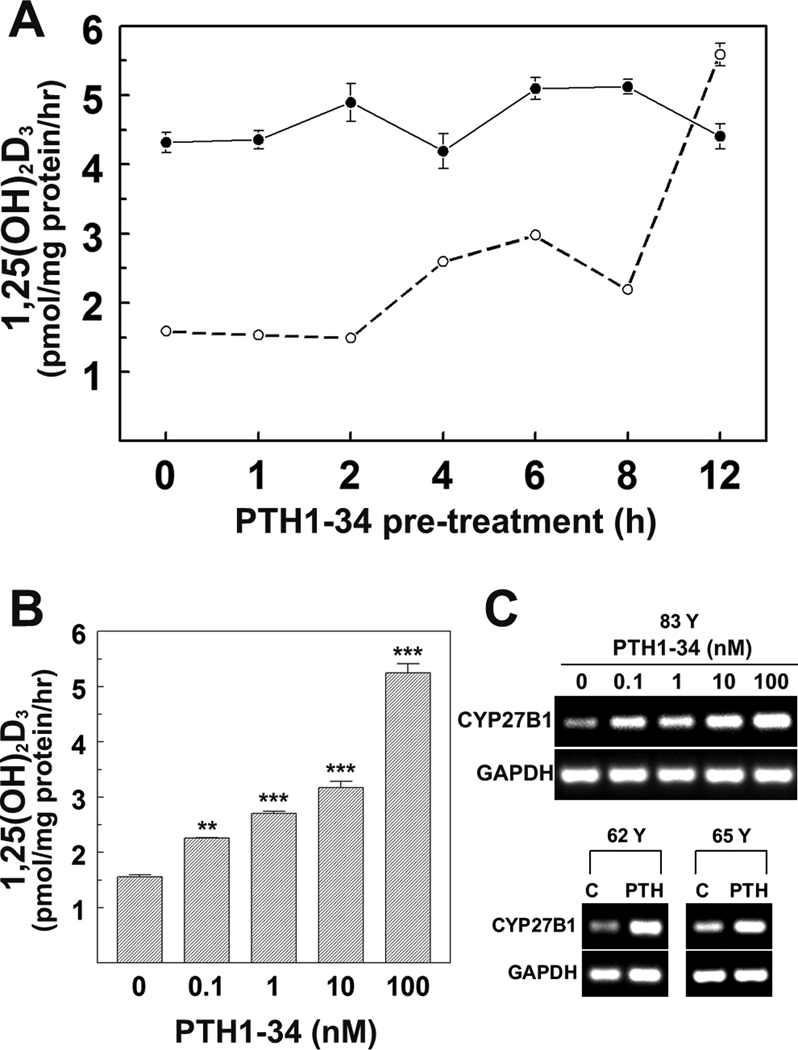
FIG. 3. Dose- and time-dependent effects of PTH1-34 on vitamin D 1α-hydroxylase activity and expression in hMSCs.
(A) Comparison time-course of PTH1-34 effects on 1,25(OH)2D3 production in hMSCs from two subjects (42 Y and 83 Y). Cells were treated with 100 nM PTH1-34 for 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 hours in serum-free α-MEM. For synthesis of 1,25(OH)2D3, they were changed to serum-free α-MEM supplemented with 1% ITS+1, 10 µM 1,2-Dianilinoethane (N,N’-diphenylethylene-diamine) with or without 1,000 nM 25OHD3 for another 24 hours. Cellular 1,25(OH)2D3 production was determined by EIA. Results are presented as Mean ± SEM (3 replicate wells).
(B) Dose-response of PTH1-34 on 1,25(OH)2D3 production in hMSCs (83 Y). Cells were treated with 0, 0.1, 1, 10, or 100 nM PTH1-34 for 12 hours in serum-free α-MEM, then changed to serum-free α-MEM supplemented with 1% ITS+1, 10 µM 1,2-Dianilinoethane (N,N’-diphenylethylene-diamine) with or without 1,000 nM 25OHD3 for another 24 hours. Cellular 1,25(OH)2D3 production was determined by EIA. Results are presented as Mean ± SEM (3 replicate wells, ANOVA, **p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
(C) Gel electrophoretograms show RT-PCR products of CYP27B1 and GAPDH in hMSCs (83 Y) with 0, 0.1, 1, 10, or 100 nM PTH1-34 and hMSCs from 62, 65 years old subjects (62 Y and 65 Y) with 100 nM PTH1-34 for 8 hours in standard growth medium (10% FBS-HI).