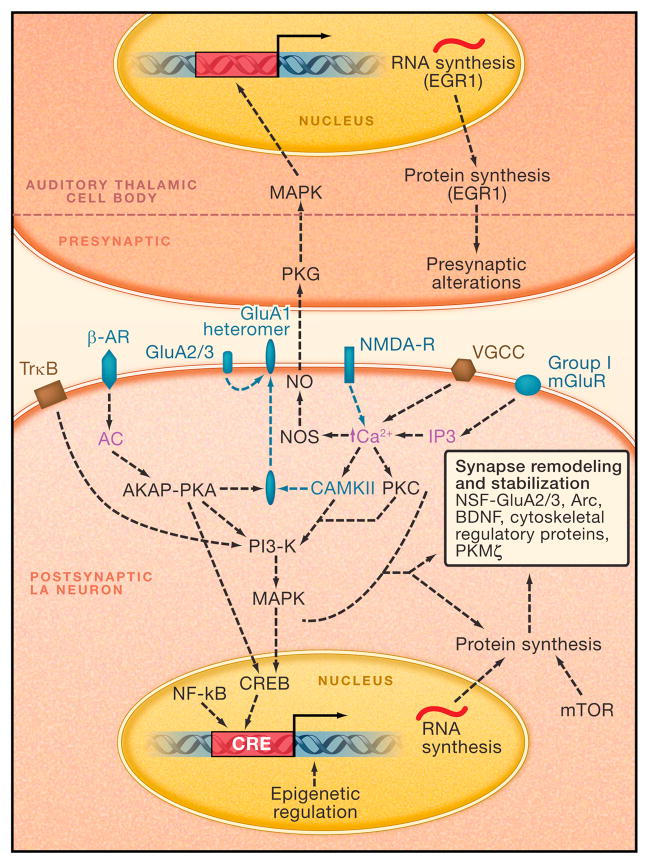
FIGURE 3. Working Model of Molecular Processes in the LA Mediating Acquisition and Consolidation of Fear Memories.
All dotted lines denote hypothetical pathways. Molecules and processes in green are known to be involved in the acquisition of fear conditioning. Molecules and process in black are known to be involved specifically in the consolidation or maintenance of fear conditioning. Purple labels denote molecules or elements whose role is not established for fear conditioning, but are part of an established intracellular signaling pathway. Abbreviations: AC, adenyl cyclase; AKAP, A-kinase anchoring protein; Arc, activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein; β-AR, Beta Adrenergic Receptor; BDNF, Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor; Ca2+, Calcium; CaMKII, Ca2+/Calmodulin (Cam) Dependent Protein Kinase II; CREB, cAMP Response Element (CRE) binding protein; EGR-1, early growth response gene 1; GluA1, Glutamate AMPA Receptor Subunit 1; GluA2/3, Glutamate AMPA Receptor Subunit 2 and 3 heteromer; IP3, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate; MAPK, Mitogen Activated Protein Kinase; mGluR, Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor; mTOR, Mammalian Target of Rapamycin; NF-kB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells NMDA-R, N-methyl-d-aspartate Glutamate Receptor; NO, Nitric Oxide; NOS, Nitric Oxide Synthase; NSF, N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor; PI3-K, phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase; PKA, Protein Kinase A; PKC, Protein Kinase C; PKG, cGMP-dependent protein kinase; PKMζ, protein kinase M ζ; RNA, Ribonucleic Acid; TrkB, tyrosine kinase B; VGCC, Voltage Gated Calcium Channel