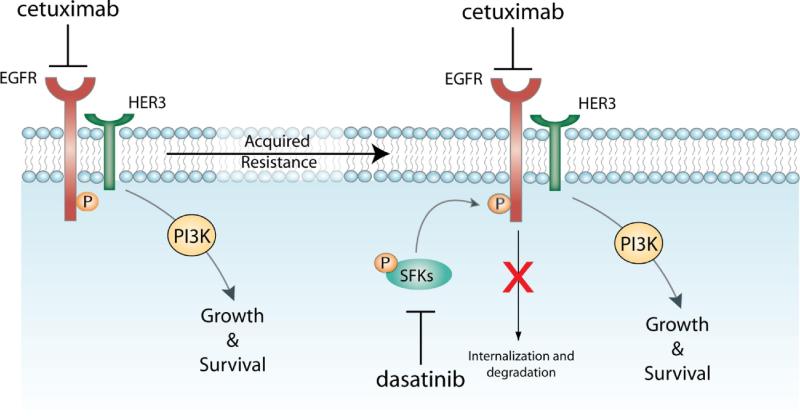
Figure 3. Potential mechanisms of acquired-resistance to cetuximab.
Cells that acquire resistance to chronic cetuximab therapy dysregulate the Cbl/ubiquitination of the EGFR(58). This modulation of internalization and degradation of the receptor results in increased steady-expression of EGFR followed by increased cooperation and activation of Src Family Kinases (SFKs). This cooperation between SFKs and the EGFR results in resistance to cetuximab therapy. Blockade using the SFK inhibitor dasatinib re-sensitizes cetuximab-resistant cells to cetuximab therapy.