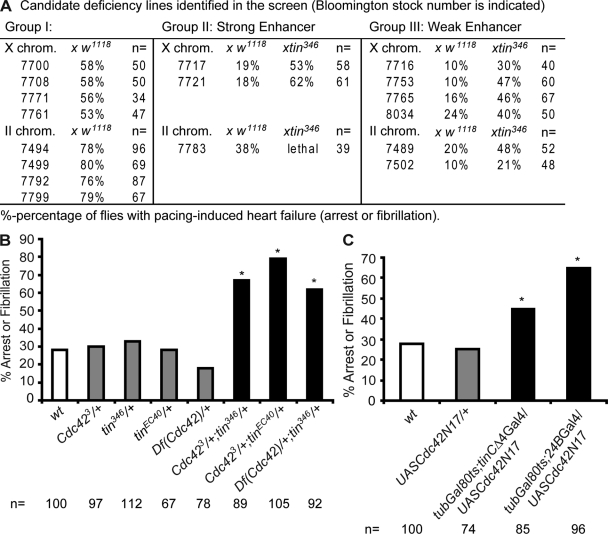
Figure 1.
Genetic screen identifying Cdc42. (A) Candidate deficiency lines interacting with tin346 (susceptibility to pacing-induced heart arrest or fibrillation). (B) Genetic interaction between tinman, Cdc42, and deficiency 7721. Cdc42+/−;tin+/− flies show dramatic increase in pacing-induced heart arrest or fibrillation rate compared with Cdc42+/− or tin+/− (Chi square analysis: *, P < 0.01). (C) TARGET-mediated overexpression (see Materials and methods) of dominant-negative Cdc42 (Cdc42N17) in the adult heart results in elevated heart dysfunction (*, P < 0.01). Each bar in B and C represents a single experiment. n, number of flies tested.