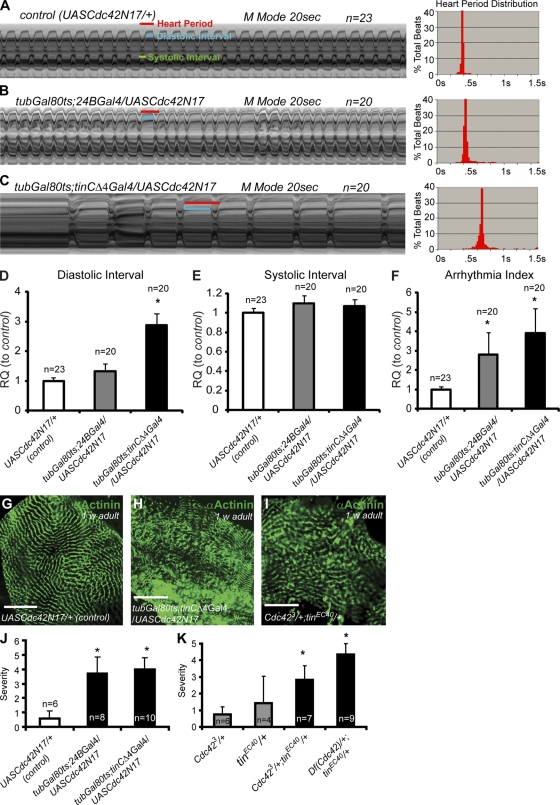
Figure 2.
Cdc42 is required for adult heart function in flies. (A–C) Cardiac M-mode traces prepared from high speed movies of semi-intact flies. (A) M-mode from control flies shows a regular beating pattern. (B and C) Arrhythmic heart beats are evident in flies overexpressing Cdc42N17 using tinCΔ4-Gal4 (G) or 24BGal4 (H). (A′–C′) Heart period histograms. (D–F) Statistical analysis of Cdc42N17 mutant heart contractions (relative quantification [RQ] compared with control). Disruption of Cdc42 in the adult heart results in longer diastolic but not systolic intervals (D and E) and in increased incidence of arrhythmias (F). Error bars represent SEM. (G–I) α-Actinin labeling of the adult heart (one segment). Cdc42N17 adult heart or Cdc42, tinman double heterozygotes show disruption of cardiomyocyte myofibrillar alignment. Bars, 50 µm. (J and K) Quantification of abnormalities in Cdc42N17 and Cdc42+/−;tin+/− hearts. Severity is determined by the average number of segments with significant abnormal myofiber structure. n, number of flies tested. Unpaired Student's t test: *, P < 0.05.