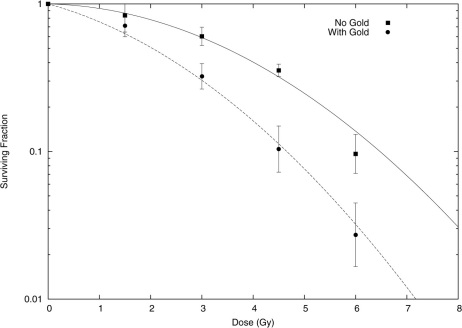
Figure 6. Experimentally observed cell survival for MDA-231 cells exposed to 160 kVp X-rays with (circles) and without (squares) exposure to 500 µg/mL of 1.9 nm gold nanoparticles, taken from10.
In the original analysis, this data was fitted using a conventional linear-quadratic model, to determine if a radiosensitising effect was observed. Here, the data is used to investigate whether the model presented in this work is capable of accurately quantifying the sensitising effects of GNPs. To that end, only the control data was fitted to directly using a linear quadratic, which gave α = 0.019 ± 0.025, β = 0.052 ± 0.007 (solid line). These parameters were used, together with modelled microscopic dose in the vicinity of a 1.9 nm GNP exposed to 160 kVp X-rays, in the Local Effect Model to predict the behaviour of the cells which were exposed to gold nanoparticles, without reference to the experimentally observed results. These theoretical predictions are plotted as the dashed line. The agreement is very good, substantially better than simple energy absorption considerations which predict an increase in damage of just 5% for this gold concentration, which suggests that the microscopic dose in the vicinity of GNPs is a significant contribution to experimentally observed GNP dose enhancement.