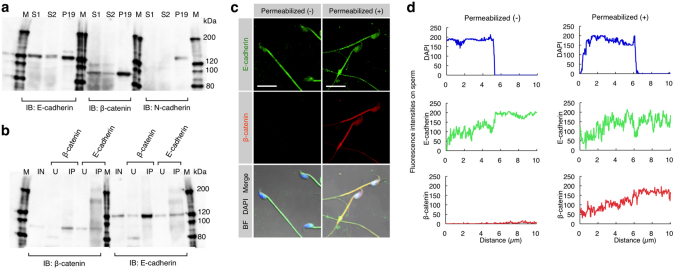
Figure 2. Expression of E-cadherin and β-catenin and their interaction in sperm.
(a) Expression of E-cadherin and β-catenin in epididymal sperm. E-cadherin and β-catenin, but not N-cadherin, in the sperm were detected by immunoblotting (IB). Sperm (S1 and S2) were collected from the epididymis of two males and used for IB. Extracts from P19 cells were used as a positive control. IB was performed using anti-E-cadherin, anti-β-catenin or anti-N-cadherin mAbs. M, molecular weight markers. (b) Interaction between E-cadherin and β-catenin in sperm. Extracts from the sperm (used as input sample (IN)) were immunoprecipitated by anti-E-cadherin or anti-β-catenin mAb. The precipitates (IP) and unbound extracts (U) were immunoblotted (IB) with anti-E-cadherin or anti-β-catenin mAb. M, molecular weight markers. (c) Localization of E-cadherin and β-catenin in sperm. Unpermeabilized or permeabilized sperm were doubly immunostained with anti-E-cadherin (ECCD-2) and anti-β-catenin mAbs, and their nuclei were stained with DAPI. ECCD-2, which recognizes an epitope in the N-terminal extracellular region of E-cadherin, bound to E-cadherin without permeabilization pretreatment. Scale bar: 5 µm. (d) The fluorescence intensity profiles of E-cadherin and β-catenin in sperm shown in (c). Fluorescence intensities were measured after being traced on the sperm along dotted lines shown at the bottom of the panels in (c).