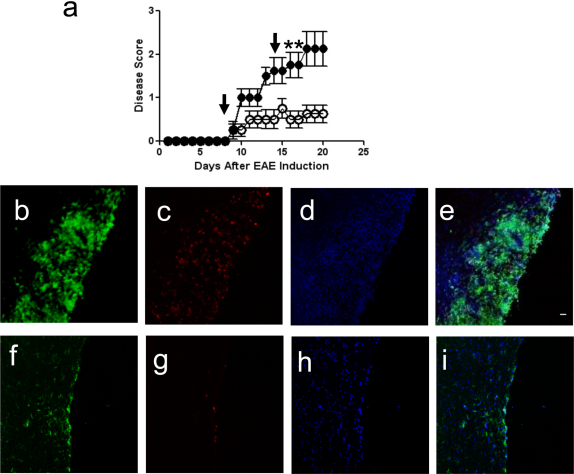
Figure 2. CPT-1 Inhibition Ameliorates Disease Activity During EAE.
(a) EAE was induced with MOG peptide. After disease induction, mice received 2 intraperitoneal injections of etomoxir 15 mg/kg on days 8 and 15 (arrows; (○)) while control mice were injected at the same time points with vehicle alone (•) (n = 4 mice per group; data are representative of three independent experiments). Disease was scored as follows; 0 = no disease, 1 = limp tail, 2 = hind- limb paresis, 3 = hind-limb paralysis, 4 = hind/forelimb paralysis, and 5 = death. Etomoxir-treated-mice show decreased disease compared to controls (*p<0.05). (b–i) Fluorescence immunohistochemistry of inflammatory lesions in spinal cords from vehicle-treated (B–E) and etomoxir-treated EAE mice (f–i). Sections are stained with FITC-conjugated anti-CD11b to detect macrophages and activated microglia (b, f), and PE-conjugated anti-CD4 to detect CD4+ T-cells (c, g), and counterstained with DAPI (d, h). Merged panels are shown in (e) and (i). Scale bar is 50 microns.