Figure 6. Predominant role of PDE1 in the temporal context-dependent CaMKII inhibition and RP suppression.
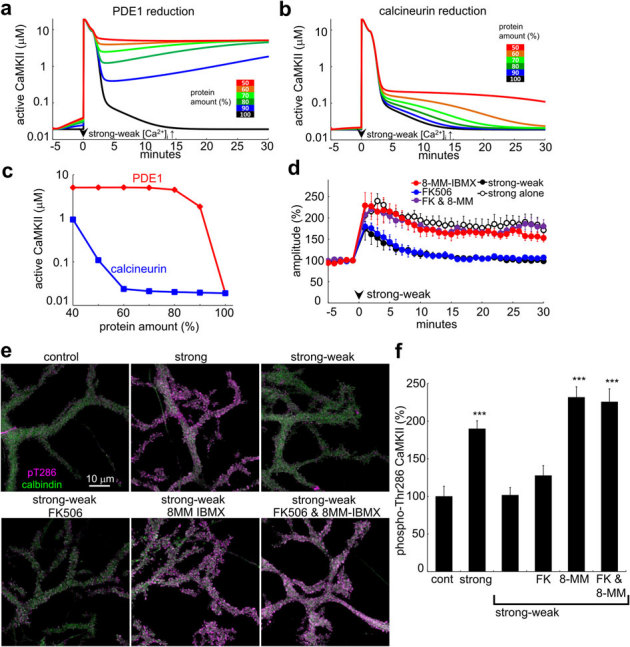
(a, b) Simulated time courses of amount of active CaMKII in response to the strong-weak sequence of [Ca2+]i increase under the condition of decreased amount (as indicated by color) of PDE1 (a) or calcineurin (b) in the model. (c) Relation between the amount of active CaMKII at 30 minutes and the amount of PDE1 or calcineurin in the model. (d) Time courses of GABA response amplitudes before and after the strong-weak sequence of conditioning depolarization with or without a selective PDE1 inhibitor, 8-MM-IBMX (20 μM), and/or a specific calcineurin inhibitor, FK506 (400 nM). n = 5 for each. The time course of RP induced by the strong alone conditioning depolarization is also shown for comparison. (e, f) Representative immunofluorescent images (e) and normalized intensity (f) of active CaMKII phosphorylated at Thr286 (magenta) in PCs before (control) or 30 minutes after the conditioning treatments with high K+-containing external solution. Green color shows the calbindin signal used as a marker for PCs. Strong depolarization treatment with 50 mM K+ was applied for 10 seconds, without (strong) or with (strong-weak) subsequent weak depolarization treatment with 10 mM K+-containing solution for 5 minutes in the presence or absence of FK506 (5 μM) and/or 8-MM-IBMX (20 μM). n = 22 cells for each condition. ***: p < 0.001 by Dunnet T3 test.
