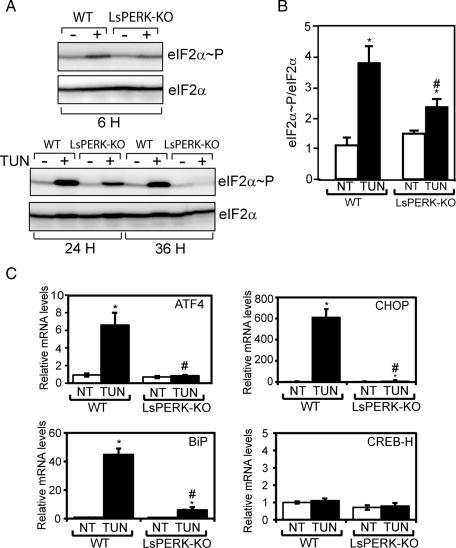
FIGURE 1:
Liver-specific knockout of PERK reduces eIF2α∼P and the ISR in response to tunicamycin treatment. (A) WT and LsPERK-KO mice received intraperitoneal injections with tunicamycin (TUN), and following 6, 24, or 36 h of exposure to this ER stress agent, the levels of eIF2α∼P and total eIF2α in livers were measured by immunoblot analyses. The + indicates treatment with tunicamycin, and the – indicates injection with only excipient. Results shown in each panel are representative of at least three independent experiments. (B) Quantification of the levels of total and phosphorylated eIF2α in the WT and LsPERK-KO livers following 6 h of treatment with tunicamycin (TUN) or with excipient (NT, no treatment). (C) The levels of ATF4, CHOP, BiP, and CREB-H mRNAs in the WT and LsPERK-KO livers exposed to tunicamycin for 6 h, or to no treatment, were measured by qPCR. * indicates statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between the levels of tunicamycin treated (TUN) and no treatment (NT) samples; # indicates statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between WT and LsPERK-KO mice. The error bar represents the SEM.