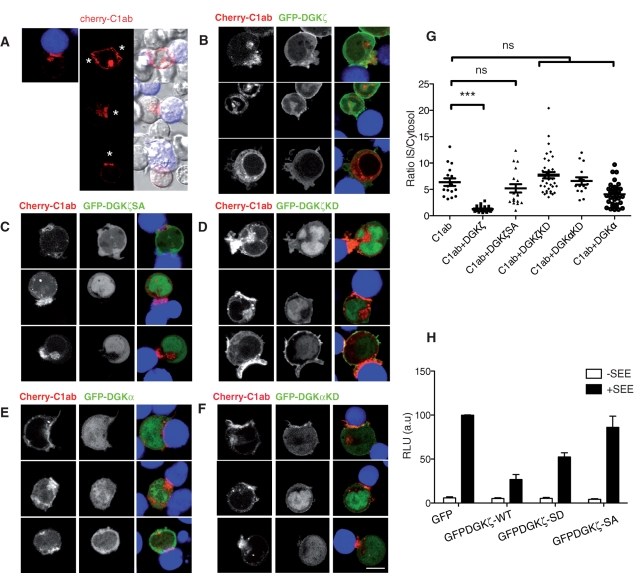
FIGURE 5:
DGK localization modulates local DAG pools. (A–F) Jurkat T cells were transfected with the tandem C1 domain of PKCθ fused to Cherry (Cherry-C1ab) alone (A) or cotransfected with GFP-tagged constructs of DGKα or ζ wild type (WT) (B and E, respectively) or mutated DGKζSA, DGKζKD, or DGKαKD (C, D, and F, respectively), to visualize DAG generation by videomicroscopy during antigen presentation. Raji B cells were treated as in Figure 4; asterisks, Raji B cell position. Representative images from different fields during in vivo imaging are shown (A–F). Bar, 5 μm. (G) Quantitative analysis of Cherry-C1ab accumulation at the IS in cells transfected with Cherry-C1ab alone or with GFP-DGK constructs taken from three individual experiments. Each dot represents the synapse:cytosol intensity ratio of Cherry C1ab after APC encounter. Bars, mean ± SEM, n ≥ 15 (***p < 0.001; Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). (H) Reporter assay for the IL-2 promoter. Jurkat T cells were cotransfected with 15 μg of IL-2 luciferase reporter/10 ng Renilla and with GFP alone or with GFP-DGKζ WT or mutant (SD or SA). At 48 h posttransfection, cells were stimulated at a 1:1 ratio with APC alone or SEE loaded (24 h). Data show mean ± SD; n = 3 from individual assays.