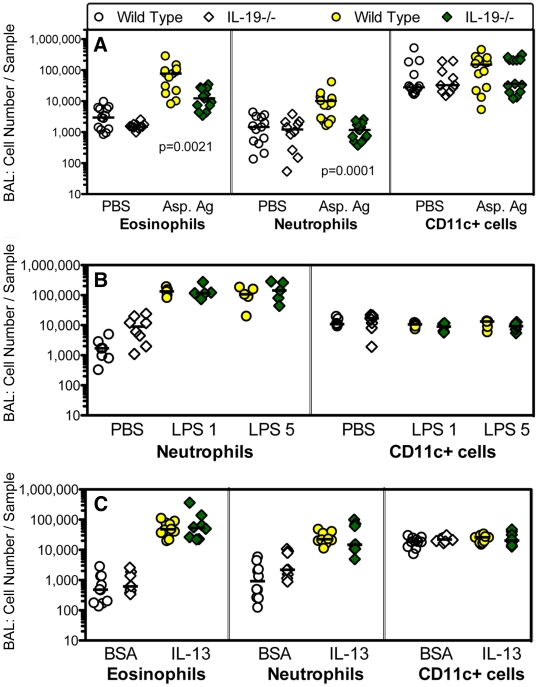
Figure 6. IL-19-/- mice have a decreased inflammatory response to a T cell-dependent challenge of the airways.
(A) Groups of IL-19-/- (diamonds) and wild type (circles) mice were primed with Aspergillus antigen and challenged with antigen intranasally (Asp. Ag, shaded symbols). (B, C) Groups of naïve mice were given lipopolysaccharide (B, LPS, 1 or 5 µg/dose as indicated) or IL-13 (C) intranasally shown as shaded symbols. Control animals received saline (PBS) or control protein (bovine serum albumin, BSA) intranasally (A-C, open symbols). Figure S1 shows the experimental schedules; Figure S2 the technique for the determination of eosinophils, neutrophils, and CD11c+ cells in the BAL by flow cytometry. IL-19-/- and wild type mice were of the BALB/c (A), or C57BL/6 (B, C) background strains. Groups of mice were pooled from 2-3 independent experiments. Individual data are shown. Horizontal lines represent medians. Significance levels were calculated with the Mann Whitney U test.