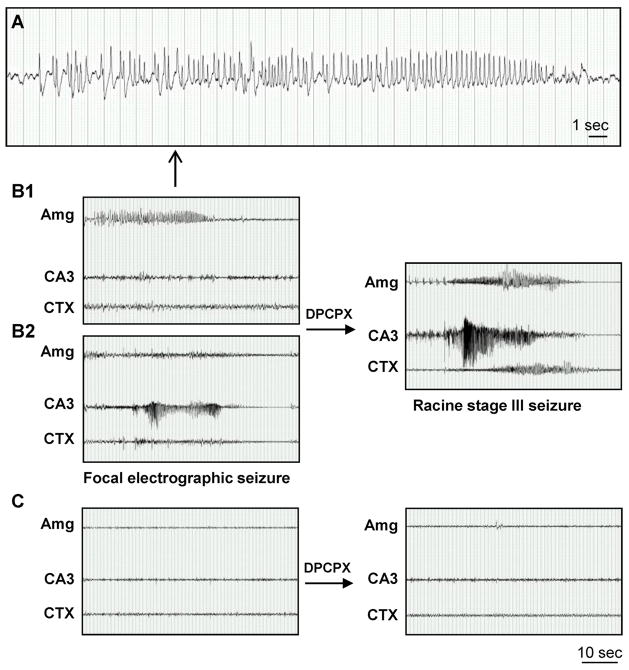
Figure 7.
Focal spontaneous seizures develop in the amygdala and CA3 three weeks after intraamygdaloid KA injection. A, High resolution EEG trace of the amygdala-originating spontaneous focal electrographic seizure depicted in panel B1. B, Recordings three weeks after KA injection from bipolar electrodes implanted into the amygdala (Amg) and CA3 and from a monopolar electrode implanted in the cortex (CTX). Note that spontaneous electrographic seizures are focal, but alternate in origin between the Amg (B1) and CA3 (B2). DPCPX injection (1 mg/kg in 20% DMSO/saline, i.p) synchronizes electrographic seizure activity in the Amg and CA3 with subsequent generalization to the CXT (right). C, Recordings from the Amg, CA3 and CTX in control saline-injected mice. Note that there was no response to DPCPX (right). Scale bars: 1 second (A); 10 seconds (B,C).