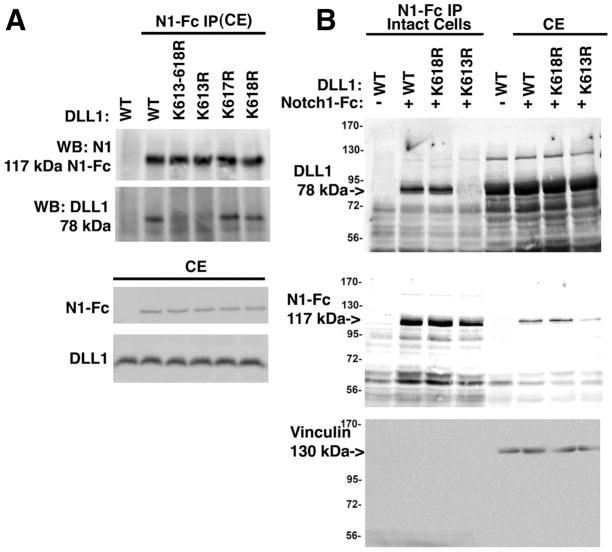
Figure 4. Residue K613 in Dll1 is important for both cis and trans interactions with Notch1.
A, HEK293 cells were transfected with wild type or mutant Dll1 as indicated. After 36 hrs. cell lysates were prepared and then incubated with 1 μg/mL recombinant Notch1-Fc fusion protein pre-complexed to protein G agarose. Western blotting was carried out to detect Dll1 and Notch1-Fc using anti-Delta (sc-9102) or anti-Notch1 (sc-9170) antibodies. To confirm the expression of proteins western blotting of 25 μg total cell extract was used. B, HEK293 cells were transfected with wild type or mutant Dll1 as indicated. After 36 h, the intact cells were incubated with 1 μg/mL recombinant Notch1-Fc fusion protein for 18h at 4°C, the intact cells were washed to remove unbound Notch1-Fc, lysed and then equal amounts of total protein were incubated with protein G agarose. To confirm the presence of the relevant proteins, an aliquot representing 25 μg of the total cell extract (CE) was reserved prior to immunoprecipitation and analyzed in parallel. Western blotting was carried out as in ‘A’ and vinculin was used to confirm that equivalent amounts of CE were used for analysis. Representative blots are shown for each panel; n=3. IP, immunoprecipitation, CE, cell extract, N1-Fc, Notch1 extracellular domain-Fc fusion protein.