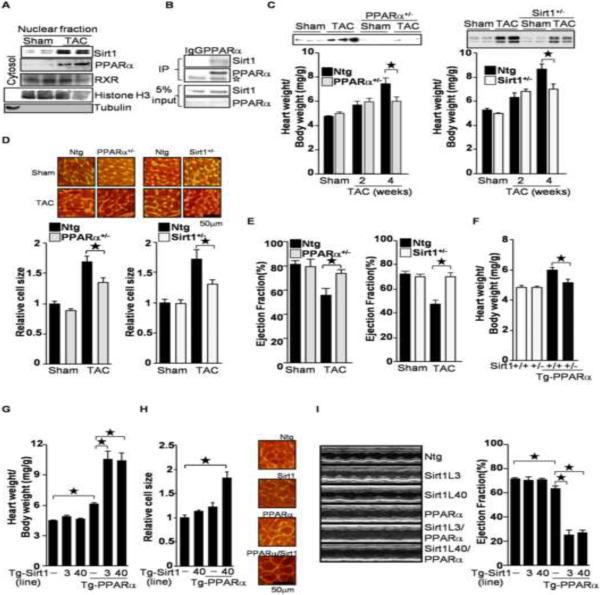
Figure 1.
PPARα and Sirt1 are involved in pressure overload(PO)-induced cardiac hypertrophy. (A) PO induces co-upregulation of PPARα and Sirt1. Nuclear fractions were prepared from wild type mice subjected to transverse aortic constriction (TAC) for 4 weeks. Anti-histone H3 and tubulin antibodies were used to show nuclear and cytosolic fractions, respectively. (B) Sirt1 was co-immunoprecipitated with PPARα from primary cultured cardiac myocytes. Open asterisk represents IgG. (C–E) Haploinsufficiency of PPARα and Sirt1 attenuates PO-induced cardiac hypertrophy (C–D) and systolic dysfunction (E). PPARα+/− and Sirt1+/− mice were subjected to 4 weeks of TAC. (C) The heart weight/body weight ratio was measured. Heart lysates were subjected to Western blot analyses with anti-PPARα and anti-Sirt1 antibodies. (D) After 4 weeks of TAC, cell size was measured using WGA staining. Representative images are shown. (E) After 4 weeks of TAC, ejection fraction was measured by echocardiography. (F) Haploinsufficiency of Sirt1 normalizes PPARα-induced cardiac hypertrophy. (G–H) Co-overexpression of PPARα and Sirt1 induces cardiac hypertrophy. Heart weight/body weight ratio and myocytes cell size were measured. (I) Ventricular dysfunction in Tg-PPARα/Tg-Sirt1 bigenic mice was evaluated by echocardiographic measurements. Representative M-mode echocardiographic images of the left ventricle and ejection fraction are shown. The numbers of mice examined in each experimental group were: 4–12 (C), 3–8(D), 6–14 (E), 3–6 (F), 9–21 (G), 3 (H), and 7–19 (I). Error bars represent S. E. M.