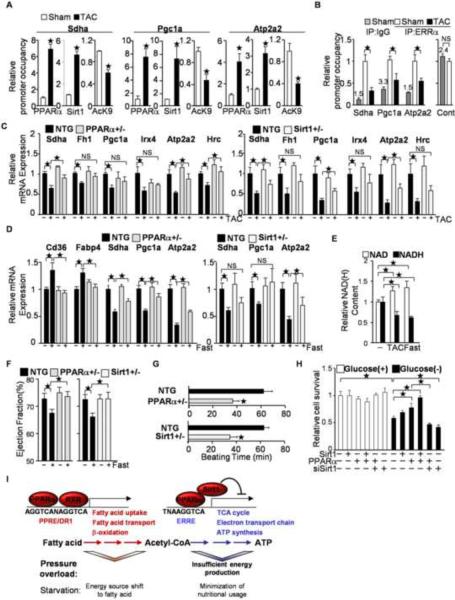
Figure 7.
Involvement of PPARα/Sirt1-mediated ERRE suppression in pressure overload(PO)-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fasting. (A–B) After 4 weeks of TAC, ChIP assays were performed with anti-Sirt1, anti-PPARα and anti-histone H3 acetyllysine 9 specific antibodies (A) or anti-ERRα antibody (B) (N=4–8). PPARα and Sirt1 bind to the single hexad motifs of HREs in response to PO in the heart (A), whereas the occupancy of ERRα on the ERRE decreases (B). (B) The control region corresponds with Pgc1a (−137 to 0). The number above the control IgG column represents raw data of the copy number (×1000) (C) Haploinsufficiencies of PPARα and Sirt1 attenuate PO-induced downregulation of ERR target gene expression. The expression levels of the indicated genes were examined by quantitative PCR (N=4–12). (D) PPARα/Sirt1-mediated ERRE suppression is a fasting response. PPARα+/− and Sirt1+/− mice were subjected to fasting for 24 hours. The expression levels of the indicated genes were examined (N=8–20). (E) The NAD/NADH ratio is increased by 24 hours of fasting and 4 weeks of TAC (N=4–8). (F) Fasting-induced attenuation of systolic function is mediated by PPARα and Sirt1. Ejection fraction was measured in PPARα+/− and Sirt1+/− mice after 24 hours of fasting. (N=18–20). (G) Hearts were isolated from PPARα+/− and Sirt1+/− mice and subjected to the Langendorff perfused heart experiment without any nutrients in the perfusate. The duration of consecutive beating was evaluated in each heart (N=7–9). (H) PPARα and Sirt1 prolong survival of cultured cardiac myocytes under glucose-free conditions. The indicated expression or knockdown was introduced with adenovirus vectors. Cell viability was evaluated with Trypan blue dye exclusion following incubation with complete or glucose-free medium for 72 hours (N=3). Error bars represent S. E. M. (I) Schematic representations of the regulatory roles of PPARα, Sirt1 and RXR on the PPRE and the ERRE during pressure overload and fasting. PPARα shifts the energy source to fatty acids through PPRE activation, and minimizes nutritional usage through ERRE suppression, with the functional binding partners RXR and Sirt1, respectively. PPARα-mediated ERRE suppression is triggered by pressure overload, which exacerbates cardiac dysfunction due to insufficient energy production.