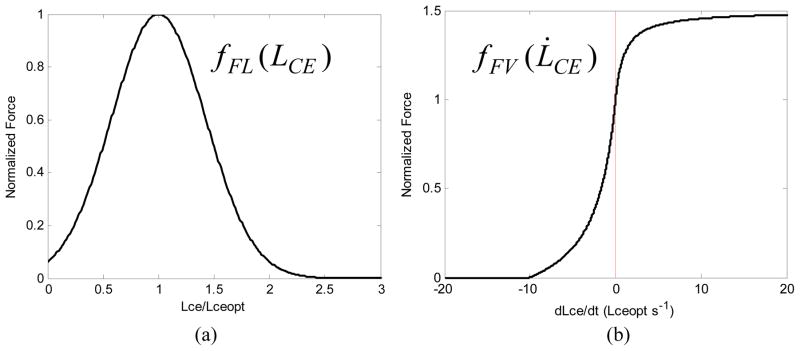
Fig. 2.
(a) Typical force-length relationship for muscle fibers. Lceopt is the fiber length at which the highest force can be generated; (b) Typical force-velocity relationship for muscle fibers. Negative velocities represent shortening (concentric contraction), positive velocities represent lengthening (eccentric contractions). The maximum shortening velocity is typically around 10 fiber lengths per second [15], and the force does not exceed 150% of the (isometric) force at zero velocity.