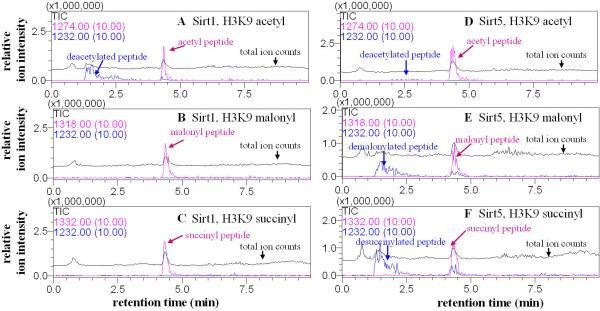
Fig. 2.
Sirt5 catalyzed the hydrolysis of malonyl and succinyl lysine. The enzymatic reactions were analyzed by LC-MS. Pink traces showed the ion intensities (10× magnified) for the masses of the acyl peptides (acetyl, m/z 1274.0; malonyl, m/z 1318.0; succinyl, m/z 1332.0) and blue traces showed the ion intensities (10× magnified) for the mass of the deacylated peptide (m/z 1232.0). Black traces showed the ion intensity for all masses from 100-2000 (total ion counts or TIC). With Sirt1, hydrolysis was observed for the acetyl peptide (A), but not malonyl (B) or succinyl (C) peptide. With Sirt5, hydrolysis of the acetyl peptide was barely detectable (D) while hydrolysis of the malonyl (E) and succinyl (F) peptides were obvious.