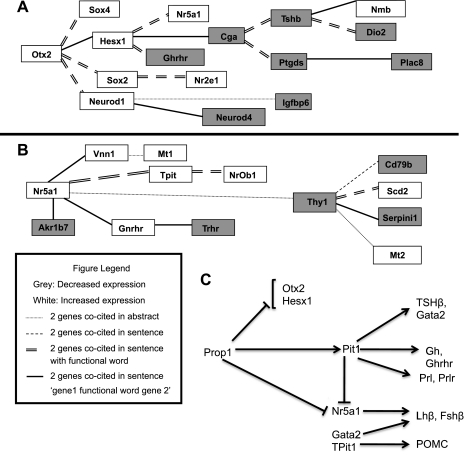
Fig. 4.
A, B: potential Prop1 and Pit1 gene expression networks. Pathways generated using Genomatix Bibliosphere software based on genes differentially expressed in Prop1df/df relative to wild type and Pit1dw/dw relative to wild-type microarrays. White boxes signify increased gene expression and grey boxes signify decreased gene expression. Connecting lines are based on Genomatix Bibliosphere Co-citation Filter, which connects genes based on co-citation frequency and specificity levels. The following lines represent the different levels of specificity: dotted line represents 2 genes co-cited within an abstract; dashed line represents 2 genes co-cited in the same sentence; double-dashed line represents 2 genes co-cited in the same sentence with a functional word; Single, thick line represents 2 genes co-cited in the same sentence with a functional word but restricted to the order, “gene 1 function word gene 2”. Network of genes with altered expression in Prop1 mutant related to increased Otx2 expression (A) and increased Nr5a1 expression (B). C: Prop1-directed gene pathway. Prop1 is upstream of Pit1. Pit1 is required for expansion and differentiation of a lineage of hormone producing cells in the pituitary, which includes somatotropes (GH), thyrotropes (TSH), and lactotropes (PRL). Both Prop1 and Pit1 are necessary for inhibiting the expression of Nr5a1, which in turn, along with Gata2, causes differentiation of the gonadotropes (LHβ and FSHβ). Otx2 and Hesx1 repress the expression of Prop1 at the appropriate time during development.