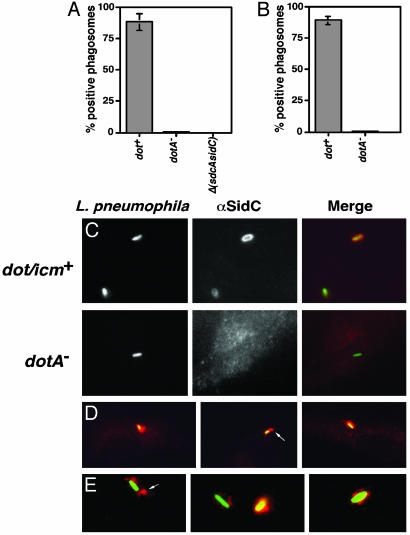
Fig. 4.
SidC is translocated by the L. pneumophila Dot/Icm system to the host cell and is localized about the phagosomal membrane. (A) Bone marrow-derived macrophages from A/J mice were infected with Lp02(dot/icm intact), Lp03(dotA–), or Lp02(ΔsdcA-ΔsidC) strain expressing GFP, respectively. One hour after infection, cells were fixed as described (10), and SidC was probed with anti-(His)6-SidC antibodies and Texas red-labeled secondary antibodies. Stained macrophages were scored for translocation of SidC by counting phagosomes that stained positively with anti-(His)6-SidC. Data shown are from two independent experiments performed in triplicate in which at least 100 phagosomes were scored per coverslip. (B) SidC staining on PNS prepared from L. pneumophila-infected U937 cells in the absence of permeabilization. Sample preparation, immunostaining, and data collection were performed as described in ref. 10 or in A. (C) DotA-dependent translocation of SidC. (Left) Bacteria expressing GFP associated with bone marrow-derived macrophage. Strains used were Lp02(dot/icm intact; Upper) and Lp03 (dotA–; Lower). (Center) Immunoprobing of infected cells with anti-(His)6-SidC. (Right) Merged images of GFP and anti-(His)6-SidC staining. (D) Limited diffusion of SidC from L. pneumophila phagosome. Shown are images of Lp02(dot/icm intact) with murine bone borrow-derived macrophage. (E) SidC is translocated across the phagosomal membrane. Shown are images of PNSs of Lp02(dot/icm intact)-infected macrophages. Bacteria and SidC are probed as above, with bacteria marked by GFP and anti-SidC marked in red.