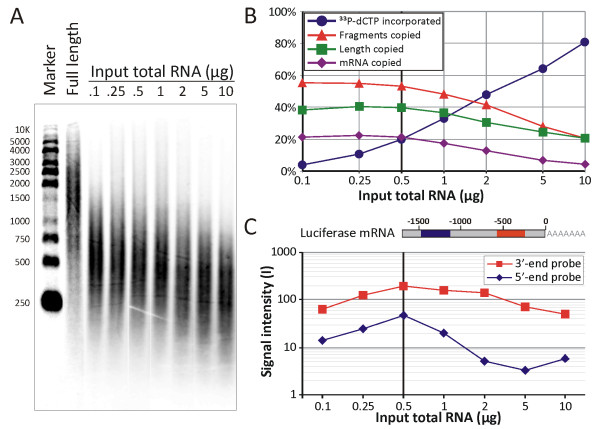
Figure 4.
Optimising reverse transcription for minimal sample input and maximal cDNA quality. A) 105 cpm of cDNA samples from reverse transcriptase reactions with the indicated amounts of input total RNA were analyzed for length distribution by electrophoresis in 1% alkaline agarose. Full length synthesis was obtained by adding cold dCTP. B) Summary of the efficiency of cDNA synthesis and 33P-dCTP incorporation based on both liquid scintillation counting measured before and after the reverse transcriptase reaction and the cDNA length distribution, calculated from the alkaline gel picture in panel A as the weighted signal intensity per fragment length. The average fragment length, the 33P-dCTP incorporation values, as well as the number of fragments generated from different amounts of input total RNA were calculated and compared to the full-length synthesised sample. As a deduction thereof, also the mass proportion of mRNA in the sample that was transcribed was calculated, taking into account the assumptions made in the methods section 'Calculations, estimates and constants'. The black vertical line indicates the amount used in all other macroarray assays. Results shown in A-B are representative for two independent experiments. C) Membrane spot intensities (± variation on duplicate spots) generated by a given amount of luciferase control transcript spiked into different amounts of mouse peritoneal macrophage total RNA when hybridised at equal cpm with two different oligo-cDNA probes on the nylon membrane. Probes were designed to bind 3'-end or 5'-end sequences. The results confirm the quality of cDNA made from 0.5 μg total RNA (black vertical line) is suitable for array hybridisation.