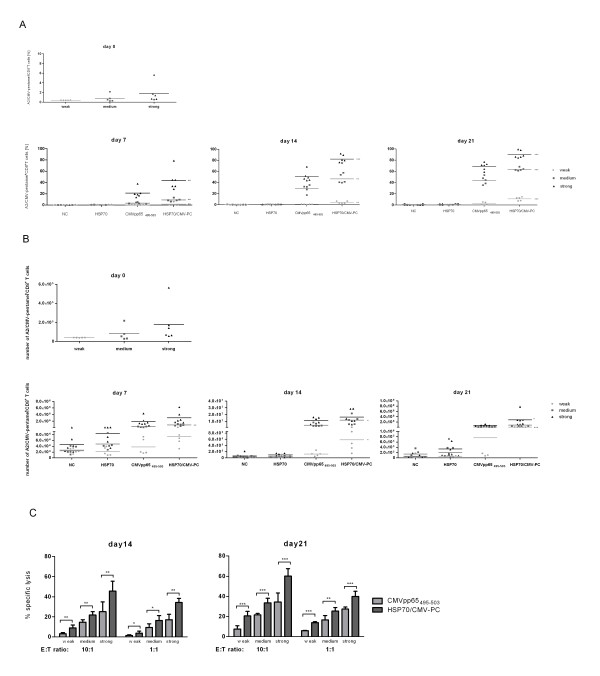
Figure 1.
HLA-A*02:01/CMV-pentamer staining, number of A2/CMV-pentamer-positive CD8+ T cells, and cytolytic function of antigen-specific CTLs stimulated with HSP70/CMV-PC and CMVpp65495-503 peptide. Frequency (A) and number (B) of HLA-A*02:01/CMV-pentamer-positive CD8+ CTLs from 16 healthy HLA-A*02:01/CMV-seropositive platelet donors on day 0 and 7, 14, and 21 days after stimulation with recombinant HSP70, CMVpp65495-503 peptide, or HSP70/CMV-PC. Cells cultured in the presence of the HSP70-peptide-binding buffer served as negative controls (NC). The 16 donors were divided into three groups (weak: n = 5, medium: n = 5, strong: n = 6) according to the frequency of generated A2/CMV-pentamer-positive CD8+ T cells on day 7. Cytolytic activity (C) of expanded T cells against antigen-loaded PBMCs after one (day 14) and two (day 21) restimulation cycles in cells from 16 healthy HLA-A*02:01/CMV-seropositive donors. CFSE-labeled PBMCs unloaded or loaded with CMVpp65495-503 peptide were used as target cells. T cells generated for 14 or 21 days in the presence of the CMVpp65495-503 peptide or HSP70/CMV-PC (effector cells) were co-cultured with target cells for 5 h at a cell ratio of 10:1 or 1:1, respectively. The basal cytotoxic activity of effector T cells induced by CMVpp65495-503 peptide or HSP70/CMV-PC against the unloaded target cells was subtracted from the cytotoxic values measured after incubation of effector T cells against CMVpp65495-503 peptide-loaded PBMCs. The results of independent experiments are expressed as mean ± SD. Asterisks shown in the Figure indicate only statistically significant differences between levels in CMVpp65495-503 peptide- and HSP70/CMV-PC-stimulated cells (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001).