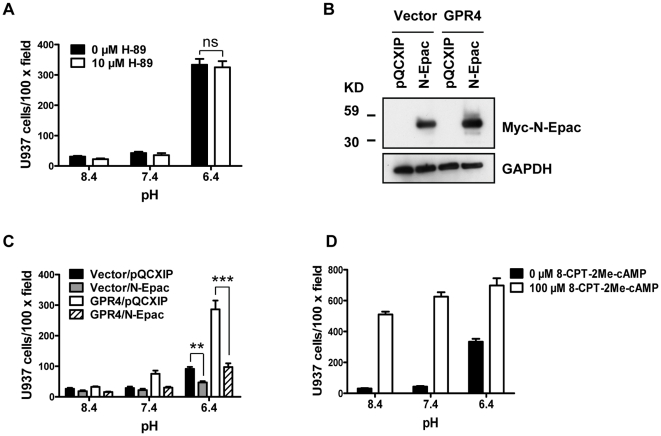
Figure 4. Epac is important for HUVEC adhesion induced by acidosis/GPR4.
(A) HUVEC/GPR4 cells were pretreated with vehicle or H-89 (10 µM) for 1 h. Cells were then treated with indicated pH media containing vehicle or 10 µM H-89 for 5 to 15 h (overnight), and the cell adhesion assay was performed as described under “Materials and Methods”. ns, not significant (P>0.05). (B) HUVEC/Vector or HUVEC/GPR4 cells were stably transduced with the myc-tagged Epac dominant-negative construct N-Epac or the control vector pQCXIP. Total proteins were extracted from HUVEC cells and subject to Western blot analysis for myc-N-Epac with anti-myc antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (C) HUVEC/Vector or HUVEC/GPR4 cells were stably transduced with the dominant-negative N-Epac or the control vector pQCXIP. Cells were treated with indicated pH media for 5 or 15 h and then the cell adhesion assay was performed. **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. (D) HUVEC/GPR4 cells were treated with indicated pH media containing vehicle or 100 µM 8-CPT-2Me-cAMP for 15 h, and then the cell adhesion assay was performed. All the above results are representative of two or more independent experiments. Error bars are the mean ± SEM.