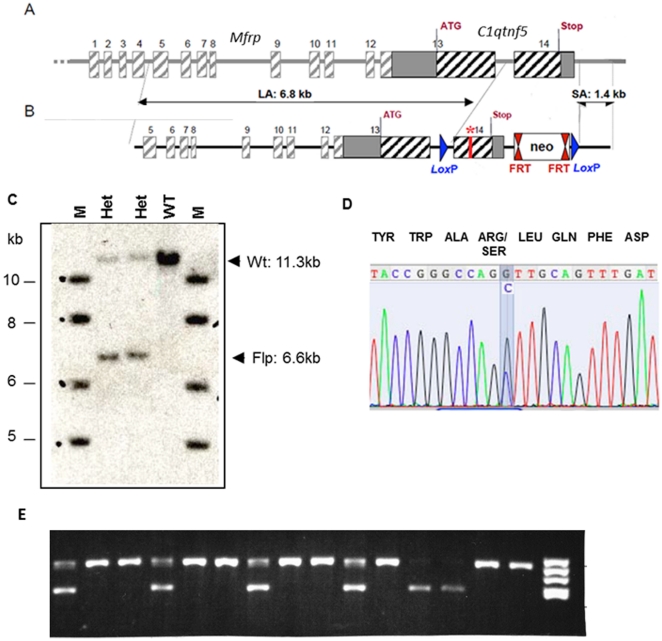
Figure 1. Introduction of the Ser163Arg mutation into the mouse C1qtnf5 gene.
A) Schematic representation of the murine Mfrp/C1qtnf5 genes. Boxes represent exons, the solid line represents intronic sequence (not drawn to scale). B) The targeting construct showing the long (6.8 kb) homology arm (LA), short (1.4 kb) homology arm (SA) and the central fragment with the Ser163Arg mutation labelled with a *. FRT: Flippase Recognition Target sites, Neo: the neomycin selection cassette. LoxP: sites flanking the introduced mutation and Neo gene, allowing subsequent Cre-recombinase-mediated deletion to generate a knockout mouse. C) Southern blot performed using genomic DNA from two heterozygous mice with a 3′ C1qtnf5 probe showing wild-type genomic DNA digested by AvrII, resulting in a 11.3-kb band, while genomic DNA containing the targeted Ser163Arg mutant showed the expected 6.6-kb band following Flp-mediated excision of the neo cassette. D) Validation of the Ser163Arg point mutation in heterozygous mice by DNA sequencing. The wild-type codon is AGC (serine), the mutant is AGG (arginine), the heterozygous mice show both alleles, highlighted in blue. E) Genotyping of tail biopsy DNA from wild-type and mutant (C1qtnf5 Ser163Arg) mice by PCR amplification of the native wild-type and mutant fragments. The primers anneal close to the FRT-sites flanking the neo cassette (see Figure 1 and Materials and Methods). The wild-type allele corresponds to the lower 432 bp band and the mutant allele to the upper 548 bp band. The gel shows genotypes in a mixture of C1qtnf5 Ser163Arg homozygous mutant (n = 9), heterozygous mutant (n = 4) and wild-type mice (n = 2). A DNA molecular weight marker V (8–587 bp; HaeIII digested pBR322 (Roche)) is shown in the right hand lane.