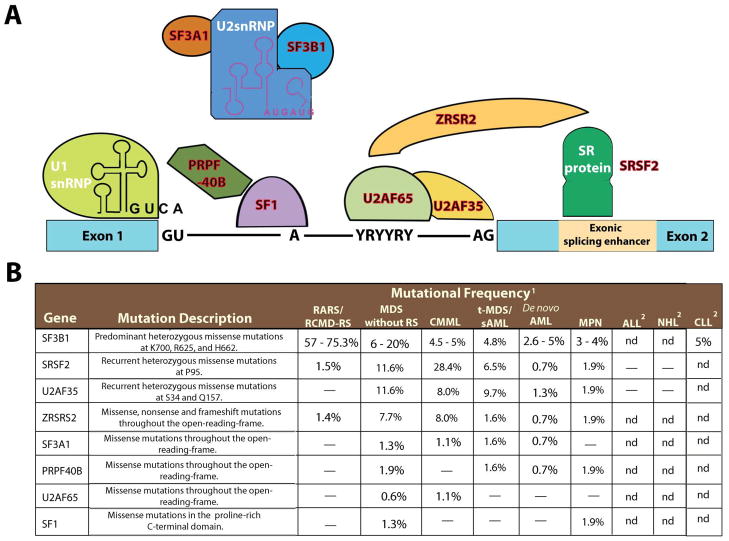
Figure 1. The spliceosome and mutations in multiple members of genes encoding spliceosomal proteins.
Five small ribonuclear protein particles (snRNPs) and over 50 accessory proteins are assembled at the exon/intron junction of pre-mRNA to form the spliceosome. The U1 snRNP binds to the 5′ splice site through base pairing between the splice site and the U1 snRNA. The branchpoint, required for the lariat intermediate, is bound by SF1 while the polypyrimidine tract is bound by the large subunit of U2AF (U2AF65). The small subunit of U2AF (U2AF35) binds to the AG at the 3′ splice site. The WW domain protein PRPF40B is thought to bind SF1 and serve in early spliceosome assembly but its functions are not well understood. Following U1 snRNP and U2AF assembly, the U2 snRNP, the U4-6 tri-snRNP and other splicing factors are assembled sequentially to form the spliceosome. SF3B1 and SF3A1 are components of U2 snRNP and it is thought that they bind pre-mRNA upstream of the intro branch site in a sequence-independent manner to anchor the U2 snRNP to pre-mRNA. Members of the serine/arginine-rich (SR) protein family bind to a nearby exonic splicing enhancer region to directly recruit splicing machinery through physical interactions with U2AF35 and ZRSR2 (a homologue of U2AF35). This interaction is critical in defining exon/intron boundaries. Members of the spliceosomal complex found to be mutated in myeloid malignancies are indicated in red in (A) and described in (B). Abbreviations: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL); chronic lymphocytic luekemia (CLL); chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML); myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN); Non-hodgkin lymphoma (NHL); refaractory anemia with ring-sideroblasts (RARS); refractory-cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia and ring sideroblasts (RCMD-RS); ring-sideroblasts (RS); secondary AML (sAML); therapy-related MDS (t-MDS).
1“–“ indicates no mutations found and nd indicates sequencing not done.
2Only regions of recurrent mutations were sequenced in these lymphoid malignancies.