Figure 2.
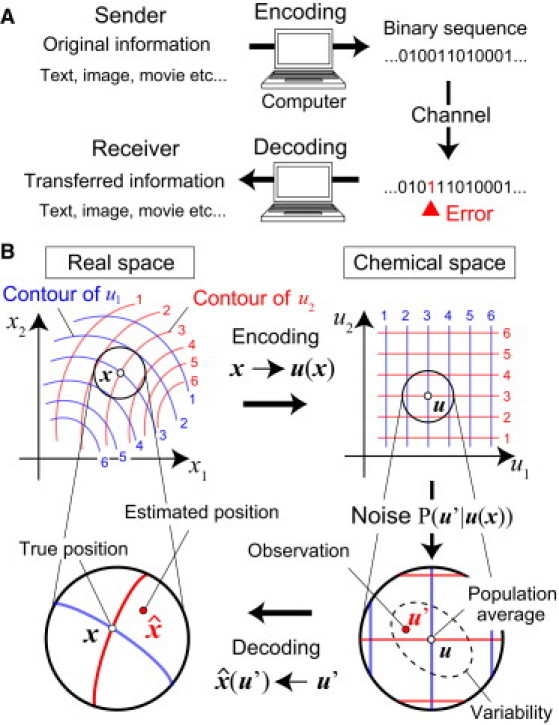
Information coding processes. (A) In information transfer between computers, the original message is converted into a binary sequence by an encoding rule. The sequence is transferred to the receiver's computer through an information channel. Finally, it is converted into the message that the sender transferred by a decoding rule. (B) In morphogenesis, a set of spatial coordinates in a tissue is converted into a set of concentrations of multiple morphogens by an encoding rule, i.e., the spatial profiles of the morphogens, u(x). Cells in the tissue read-out their spatial coordinates from the morphogen concentrations they detect through intracellular dynamics corresponding to a decoding rule. Each contour in real space corresponds to one in chemical space with the same number and color. (See Information Coding in Computer Science and Developmental Biology, and Mathematical Formulation of Positional Information Coding, for details.)
