Figure 4.
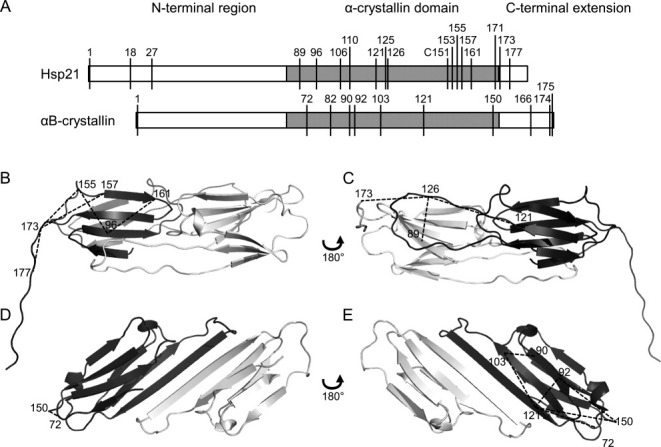
Mapping crosslink distance constraints into structures. Crosslinks listed in Tables II and III are shown here in the structures of two homologous molecular chaperone heat shock proteins, Hsp21 and αB-crystallin. A: Both protein sequences consist of an N-terminal region (white), the α-crystallin domain (gray), and the C-terminal extension (white), with the position of lysine residues indicated. B–E: Hsp21 and αB-crystallin dimers consist of two monomers (dark and light gray), of which only the α-crystallin domain is well-structured. B and C: Dimeric homology model of Hsp2122 with mapped crosslink distance constraints. D and E: Dimeric crystal structure of αB-crystallin25 (PDB ID 2WJ7) with mapped crosslink distance constraints. Each dimer is shown from two sides; one side showing the β2-β3-β8-β9 face of the dark-gray monomer (B, D), and the other side showing the β4-β5-β7 face of the dark-gray monomer (C, E). Crosslinks are indicated by dashed lines and the numbers indicate the lysines crosslinked.
