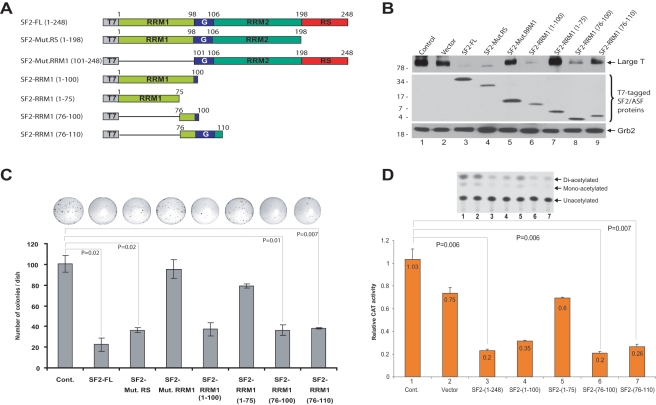
Figure 5.
Characterization of the domain of SF2/ASF important for the suppression of large T antigen expression and cell growth inhibition. (A) Schematic representation of 248 amino acid full-length SF2/ASF and the deletion mutant constructs utilized. SF2/ASF deletion mutants were cloned into pCGT7 expression vector and tagged with T7. The “G” depicts the glycine-rich domain. (B) Western blot analysis of large T antigen in HJC-2 cells transfected with the SF2/ASF mutant constructs. Expression of SF2/ASF full-length and truncated mutants was analyzed by Western blot analysis with anti-T7 antibody. Grb2 was probed as a loading control. (C) The ability of SF2/ASF full-length and various mutants to inhibit HJC-2 cell growth was analyzed by colony formation as described above in Figure 2. (D) pBLCAT3 JCV-early reporter plasmid was transiently transfected into U-87 MG cells either alone or in combination with expression plasmids encoding various deletion mutants of SF2/ASF. CAT enzymatic activities were determined, and relative CAT activities are presented as a bar graph. The autoradiograph (above the graph) represents results from one of the three independent experiments presented in the graph. The Student t test was performed to calculate P values in C and D.