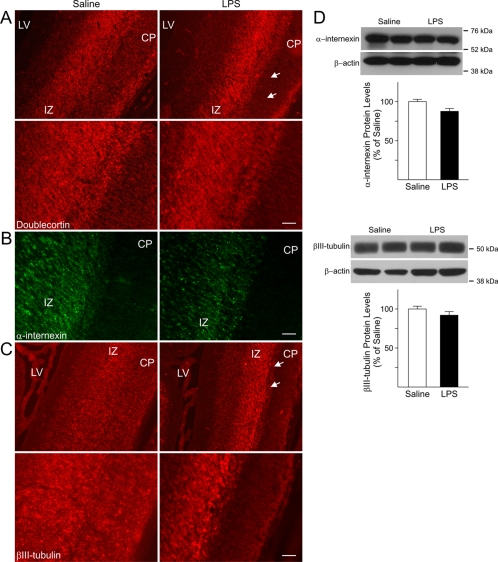
Figure 3. Abnormal distribution of markers for immature neurons in the foetal forebrain after maternal injections of LPS.
(A) Doublecortin immunoreactivity was seen in both the CP and IZ in GD18 foetuses from saline-injected dams. Conversely, doublecortin-positive cells were mostly detected in the IZ of age-matched foetuses exposed to LPS, while the CP displayed lower immunoreactivity. Lower panels are higher magnifications of the area marked by the two arrows showing the atypical distribution of doublecortin positive cells in the CP and IZ of LPS-exposed animals. (B) Expression of the immature neuronal marker α-internexin could be seen in the IZ of GD18 LPS-exposed foetuses and was almost absent in the CP as compared with age-matched control (Saline). (C) Expression of βIII-tubulin could be observed throughout the cerebral cortex in GD18 saline-exposed foetuses. In the cerebral cortex of LPS-exposed foetuses, immunoreactivity for this marker was mainly found in the IZ, while it was almost absent in the CP. Lower panels are higher magnifications of the area marked by the two arrows. Scale bar = 50 μm. LV, lateral ventricle. (D) No differences were found in the protein levels of α-internexin and βIII-tubulin measured in whole tissue lysates prepared from cerebral cortices of GD18 saline- and LPS-exposed foetuses. Values derived from the densitometric analysis were corrected for the background, normalized to β-actin and are shown as a percentage of the value for saline-exposed animals. Histograms are the means±S.E.M. for 17 foetuses from seven dams injected with saline and 18 foetuses from eight LPS-injected dams.