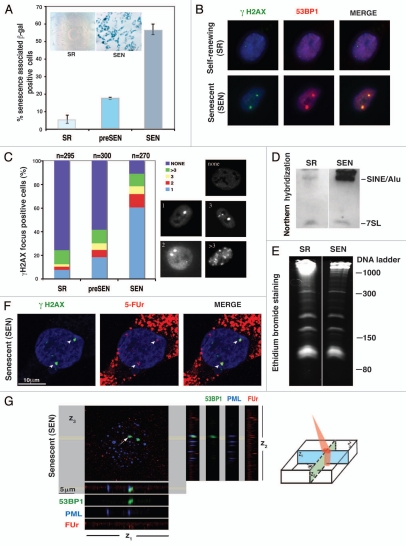
Figure 1.
Ex vivo aging of hADSCs is associated with formation of transcriptionally active persistent DNA damage foci and upregulation of transcriptional activity from Alu retrotransposons. (A) Immunohistochemical detection of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-Gal) activity. Examples of hADSCs' morphological changes (10x magnification) shown in inserts. Bar graphs correspond to percentage of SA-β-Gal positive cells with progressive ex-vivo hADSC expansion, based on three independent experiments. Error bars are standard deviations from the mean. (B) DNA damage response (DDR) in senescent hADSCs. Representative immunostaining for the persistent γH2AX (green)/53BP1 (red) foci formation upon senescence of hADSCs. (C) Quantification of accumulation of persistent DNA damage foci with ex-vivo passaging of hADSCs. γH2AX was stained with affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal antibody. Histogram indicates the percentage of the cells with 1, 2, 3 or more than 3 foci. Representative examples are shown below. Foci formation was scored in self-renewing, SR (population doubling less than 17), pre-senescent, preSEN (population doubling more than 29, but less than 38) and senescent, SEN (population doubling greater than 39) hADSCs cultures. The growth curve of ADSC in shown in the Supplemental 1B. n = total number of nuclei counted in all 3 independent experiments. (D) Alu expression in SR and SEN hADSCs. Northern hybridization of self-renewing (SR) and senescent (SEN) hADSCs with Alu oligonucleotide probe. Alu and 7SL are indicated. Total RNA of 2 µg per lane was loaded as described in Materials and Methods. (E) Ribosomal small RNAs can be seen in the ethidium bromide stained gel for loading comparison. The ssRNA ladder sizes are indicated on the right. (F) Persistent γH2AX/53BP1 foci in senescent hADSC are associated with active transcription. Senescent hADSCs were incubated with hallogenated precursor FUr for 10 min in vivo to label nuclear RNA. After fixation, cells were immunolabelled with anti-BrdU antibody (red) to detect FUr incorporation sites in combination with anti-γH2AX (green). Arrows point to co-localization of the persistent DNA damage sites upon senescence with regions of high transcriptional activity. (G) Association of DNA damage foci with transription was further verified by confocal microscopy in co-immunostaing of DNA damage foci depicted by 53BP1 antibodies (green) with PML bodies (blue) and nascent RNA (red). Representative image of a single nucleus is shown. Spatial relationship between FUr incorporation sites, 53BP1 and PML bodies in a single 5 µm confocal section is shown. Image was analyzed by Imaris software and z1, z2 and z3 planes are shown. Cartoon demonstrates the orientations of z1, z2 and z3 planes within single z-section. Confocal sectioning confirms the tight association of nascent transcripts with persistent DNA damage sites in senescent hADSCs.