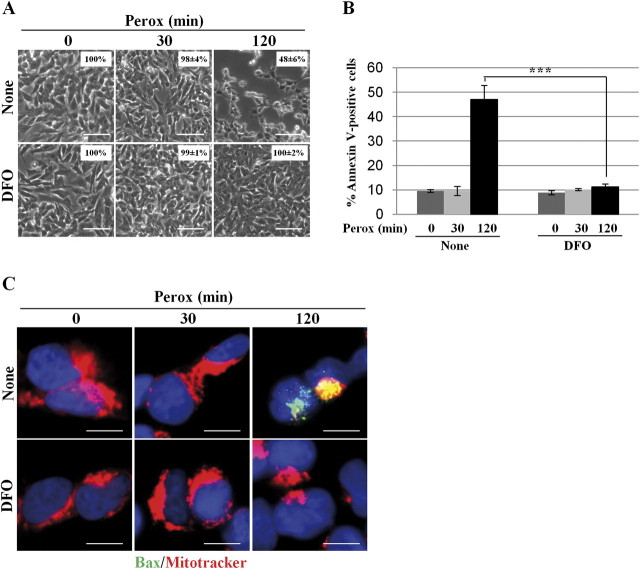
FIG. 10.
DFO inhibits bax-mediated cell death induced by H2O2. (A) SH-SY5Y cells were preincubated or not with DFO and exposed to 200μM H2O2 (perox) for 30 and 120 min. The monolayer was photographed under a phase-contrast microscope to document cell loss. The images show that DFO could prevent cell loss induced by H2O2 at 2 h. (The percentage of adherent cells is reported in the inset.) (B) SH-SY5Y cells were preincubated or not with DFO and exposed to 200μM H2O2 (perox) for 30 and 120 min. The cells were then processed for annexin V-FITC labeling and analyzed by cytofluorometry. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments in triplicate. Statistical significance between relevant treatments is reported. (C) SH-SY5Y cells adherent on coverslips and preincubated or not with DFO were incubated with 200μM H2O2 (perox) for 30 and 120 min. Cells were then processed for mitotracker and immunofluorescence staining of activated bax. At 2 h of incubation, H2O2 provoked (in about 50% of the cells) the formation of bax macroaggregates and concomitant loss of mitotracker labeling, suggestive of activation of the intrinsic death pathway. This effect was completely abolished by DFO. Images shown in this figure are representative of three independent experiments. Bar = 10 μm.