Abstract
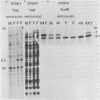
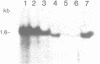
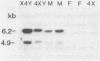
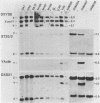
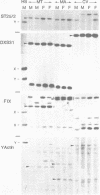
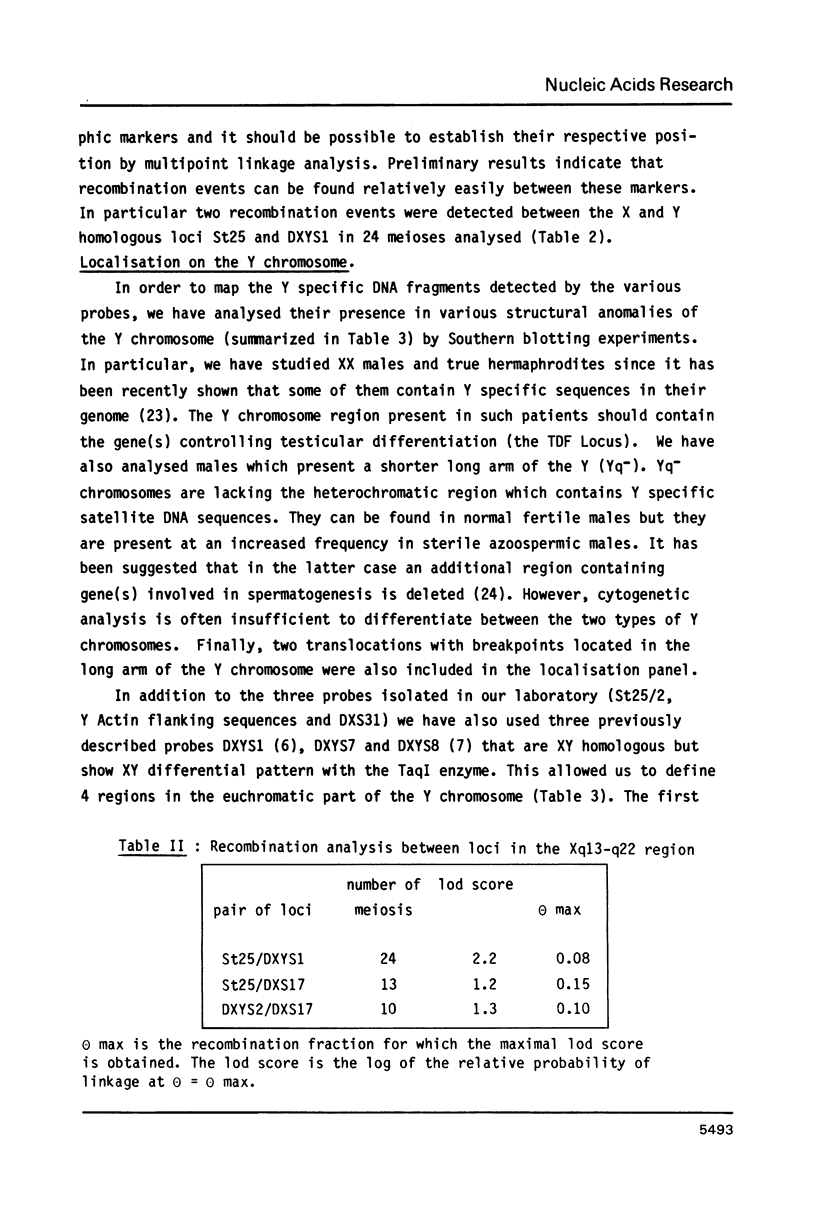
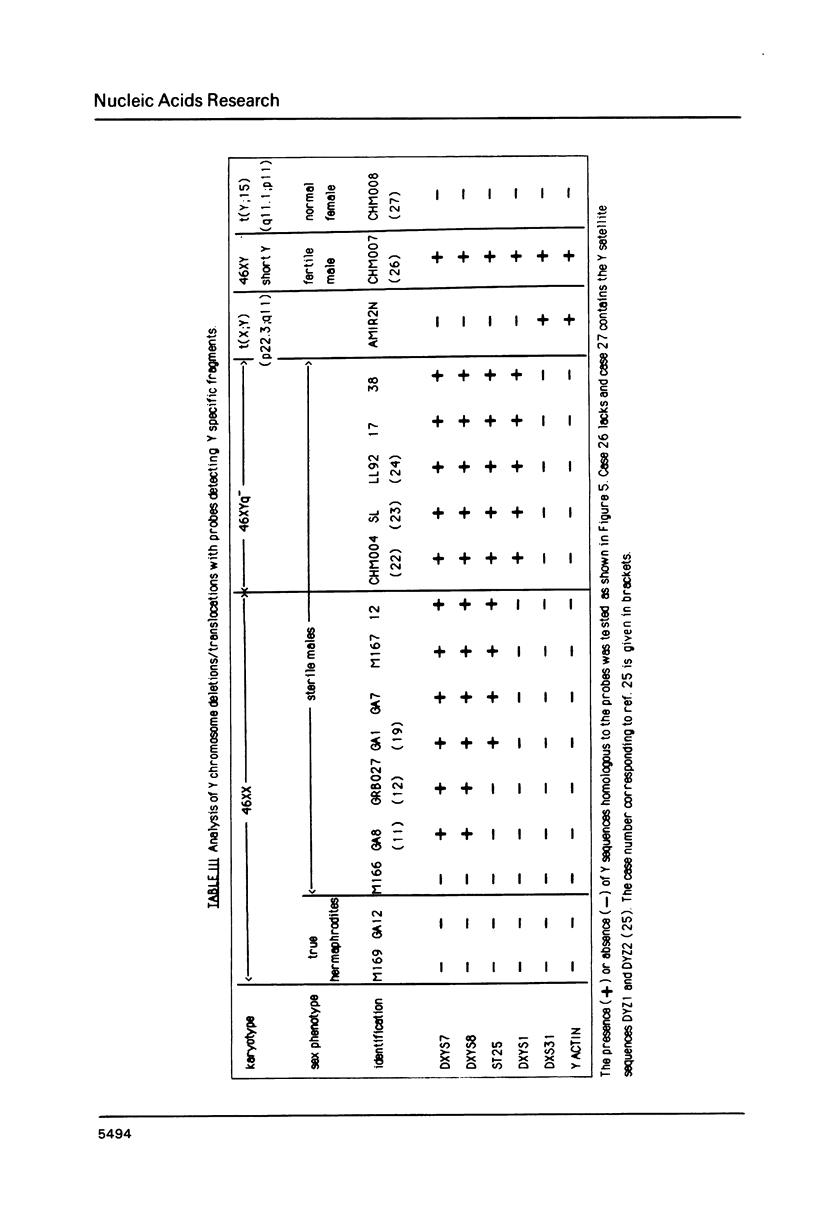
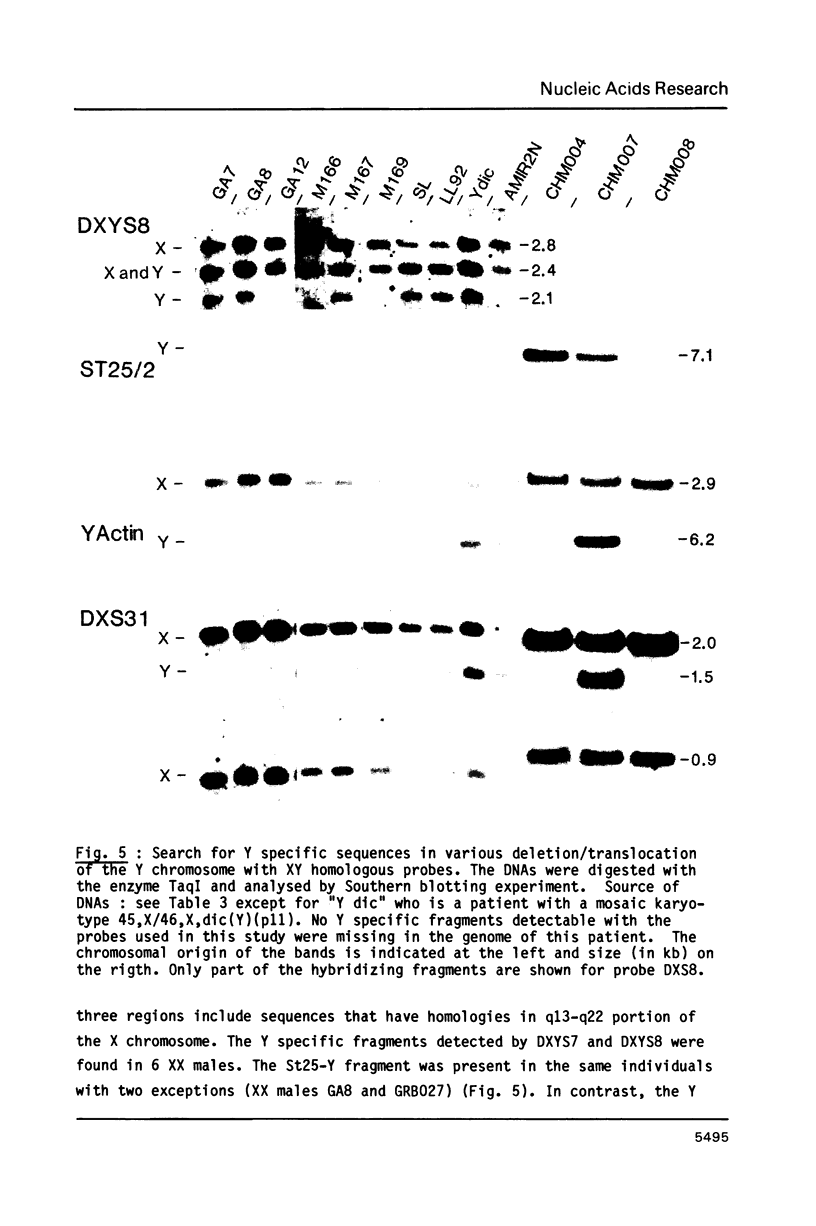
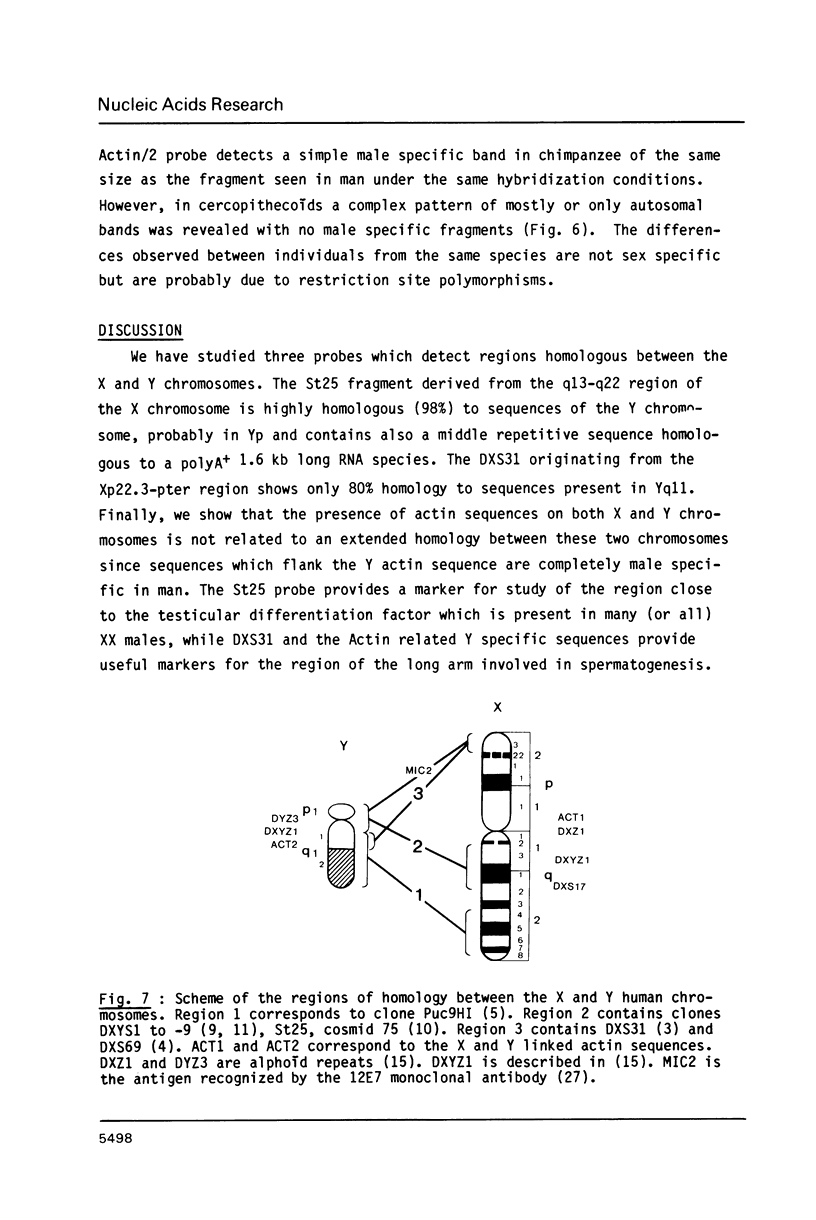
We have isolated and characterized DNA probes that detect homologies between the X and Y chromosomes. Clone St25 is derived from the q13-q22 region of the X chromosome and recognizes a 98% homologous sequence on the Y chromosome. Y specific fragments were present in DNAs from 5 Yq-individuals and from 4 out of 7 XX males analysed. An X linked TaqI RFLP is detected with the St25 probe (33% heterozygosity) which should allow one to establish a linkage map including other polymorphic X-Y homologous sequences in this region and to compare it to a Y chromosome deletion map. Probe DXS31 located in Xp223-pter detects a 80% homologous sequence in the Y chromosome. The latter can be assigned to Yq11-qter outside the region which contains the Y specific satellite sequences. ACT1 and ACT2, the actin sequences present on the X and Y chromosomes respectively, have been cloned. No homology was detected between the X and Y derived fragments outside from the actin sequence. ACT2 and the Y specific sequence corresponding to DXS31 segregate together in a panel of Y chromosomes aberrations, and might be useful markers for the region important for spermatogenesis in Yq. Various primate species were analysed for the presence of sequences homologous to the three probes. Sequences detected by St25 and DXS31 are found only on the X chromosome in cercopithecoidae. The sequences which flank ACT2 detect in the same species autosomal fragments but no male specific fragments. It is suggested that the Y chromosome acquired genetic material from the X chromosome and from autosomes at various times during primate evolution.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J. M., Davidson N. Methylmercury as a reversible denaturing agent for agarose gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80049-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Kuo M. T., Dretzen G., Chambon P. Differential nuclease sensitivity of the ovalbumin and beta-globin chromatin regions in erythrocytes and oviduct cells of laying hen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2737–2750. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C. E., Guellaen G., Geldwerth D., Voss R., Fellous M., Weissenbach J. Single-copy DNA sequences specific for the human Y chromosome. Nature. 1983 Jun 30;303(5920):831–832. doi: 10.1038/303831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop C., Guellaen G., Geldwerth D., Fellous M., Weissenbach J. Extensive sequence homologies between Y and other human chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 15;173(4):403–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne P. S. Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of Mammals. Hum Genet. 1982;61(2):85–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00274192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Brown W. A., Rappold G. A. Closely related sequences on human X and Y chromosomes outside the pairing region. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):259–261. doi: 10.1038/311259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow P., Banting G., Sheer D., Ropers H. H., Caine A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Povey S., Voss R. Genetic evidence that a Y-linked gene in man is homologous to a gene on the X chromosome. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):346–349. doi: 10.1038/302346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Camerino G., Kloepfer C., Mandel J. L., Tolstoshev P., Jaye M., De la Salle H., Lecocq J. P. Carrier detection of Hemophilia B by using a restriction site polymorphism associated with the coagulation Factor IX gene. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1491–1495. doi: 10.1172/JCI111354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guellaen G., Casanova M., Bishop C., Geldwerth D., Andre G., Fellous M., Weissenbach J. Human XX males with Y single-copy DNA fragments. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):172–173. doi: 10.1038/307172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanauer A., Levin M., Heilig R., Daegelen D., Kahn A., Mandel J. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human skeletal muscle alpha actin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3503–3516. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Hanauer A., Grzeschik K. H., Hors-Cayla M. C., Mandel J. L. Actin-like sequences are present on human X and Y chromosomes. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1803–1807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Camerino G., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. A DNA fragment from the human X chromosome short arm which detects a partially homologous sequence on the Y chromosomes long arm. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4097–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Tantravahi U., Kurnit D. M., Eisenhard M., Bruns G. P., Latt S. A. Identification and isolation of transcribed human X chromosome DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7961–7979. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D. C., Harper M. E., Love J., Botstein D. Occurrence of a transposition from the X-chromosome long arm to the Y-chromosome short arm during human evolution. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):119–123. doi: 10.1038/311119a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page D., de Martinville B., Barker D., Wyman A., White R., Francke U., Botstein D. Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiepolo L., Zuffardi O. Localization of factors controlling spermatogenesis in the nonfluorescent portion of the human Y chromosome long arm. Hum Genet. 1976 Oct 28;34(2):119–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00278879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Erickson R. P., Rigby P. W., Goodfellow P. N. Cosmid clones derived from both euchromatic and heterochromatic regions of the human Y chromosome. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1997–2003. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02081.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Erickson R. P., Rigby P. W., Goodfellow P. N. Regional localization of 3 Y-derived sequences on the human X and Y chromosomes. Ann Hum Genet. 1984 Jul;48(Pt 3):253–259. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1984.tb01022.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]