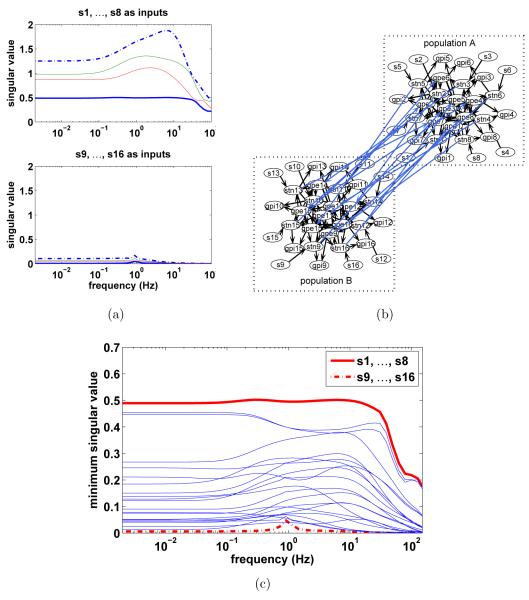
Figure 4.
Functional controllability is largely a property of the network synaptic coupling and their relative strength. (a) Example of a functionally controllable system indicated by the singular values of the transfer function matrices from {s1, … , s8} to GPi neurons 1 to 4 (upper panel); example of a almost functionally uncontrollable system with {s9, … , s16} as inputs(lower panel). (b) Network is redrawn from Figure 1(b) to demonstrate the two clusters of weakly connected populations. The four output GPi neurons to be controlled belong to population A that inputs {s1, … , s8} directly influence while {s9, … , s16} indirectly influence. (c) The minimum singular values of systems with random combinations of 8 out of 16 available simulation inputs to demonstrate the selectivity of the system across frequencies and inputs. Total 20 different random combinations are shown. The output GPi neurons are kept the same.