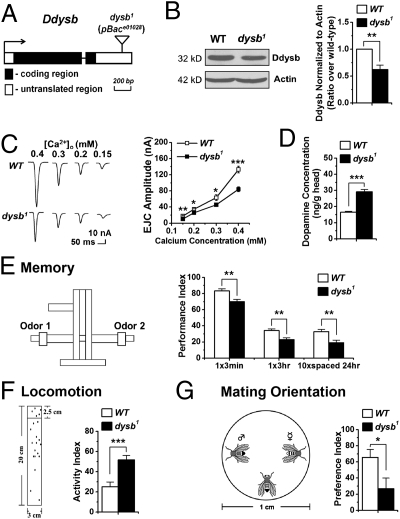
Fig. 1.
Characterization of the Ddysb mutant. (A) Transposon insertion site. (B) Representative Western blots and group data showing reduced expression of Ddysb in the head of the dysb1 mutant (t test; P = 0.007; n = 5). (C) The dysb1 mutant shows decreased EJC amplitude (t test; P = 0.002, 0.02, 0.03, and 2.1E-6 for calcium concentrations of 0.15, 0.2, 0.3, and 0.4 mM, respectively; n = 7–14). (D) Dopamine concentration in whole-head extracts of adult flies is elevated significantly in the dysb1 mutant (t test; P = 1.9E-6; n = 8–10). (E) The dysb1 mutant shows memory defects in the Pavlovian olfactory aversive conditioning (t test; P = 0.004, 0.002, and 0.009; n = 7–8). The T-maze for memory test is illustrated. (F) dysb1 mutants show dramatically increased locomotor activity (t test; P = 2E-4; n = 17). The experimental paradigm for the locomotion test is illustrated on the left. (G) The dysb1 mutant shows mating disorientations (t test; P = 0.02; n = 28–32). The mating preference assay is illustrated. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.