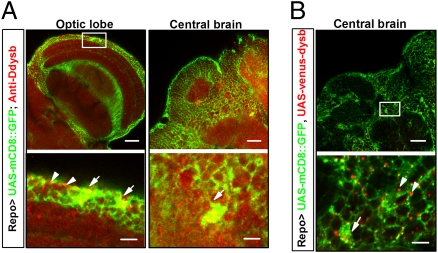
Fig. 3.
Endogenous expression of Ddysb in glial cells. Lower row shows enlarged views of boxed areas in upper row. (A) Ddysb is expressed extensively in both neurons and glia. Immunosignals of anti-Ddysb antibody (red), representing endogenous Ddysb, partially overlap (yellow) with Repo-Gal4–driven mCD8::GFP (green) at the glial cell bodies (white arrows).The dotted red signals also aggregate at the boundaries of neurons and glial processes (white arrowheads). (B) Coexpression of UAS-mCD8::GFP (green) and UAS-venus-dysb (red) in glia (UAS-mCD8::GFP/+;UAS-venus-dysb/Repo-Gal4). The immunosignals of Repo-Gal4–driven-Ddysb (red) localize at the glial cell body region (white arrow) and the boundaries of neurons and glial processes (white arrowheads), similar to the distribution of endogenous Ddysb in glia. (Scale bars: 20 μm Upper; 5 μm Lower.)