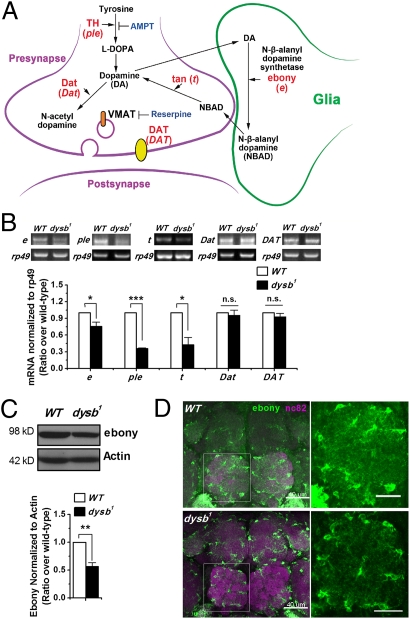
Fig. 6.
Ddysb regulates dopamine level via Ebony in glial cells. (A) Dopamine (DA) synthetic and metabolic pathway. The actions of proteins, their encoding genes, and inhibitors are shown. DAT (dopamine transporter) is a dopamine transmembrane transporter. Dat (dopamine N acetyltransferase) is an N-acetyltransferase to metabolize dopamine to N-acetyl-dopamine. VMAT (vesicular monoamine transporter) is a synaptic vesicle amine transmembrane transporter. (B) Representative RT-PCR and group data show decreased mRNA levels of ebony (e), pale (ple), and tan (t) in the dysb1 mutant (t test; P = 0.02, 1.7E-5, and 0.02; n = 4), whereas the transcripts of DAT and Dat did not have significant changes compared with WT. (C) Representative Western blot and group data showing decreased Ebony protein level in the dysb1 mutant (t test; P = 0.002; n = 7). (D) Ebony is expressed in glial cells. Neuropils were stained with mAb nc82 (magenta). Ebony immunosignals (green) were weaker in the dysb1 mutant than in the WT. (Scale bars: 40 μm Left; 20 μm Right.) *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; n.s., not significant (P > 0.05).