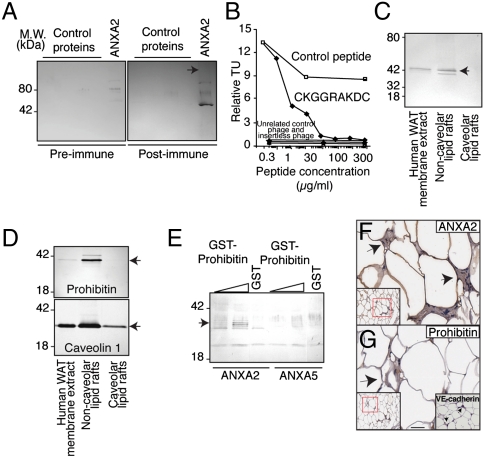
Fig. 4.
Discovery of ANXA2/prohibitin as a tissue-specific ligand-receptor targeting normal human tissue. (A) Immunoblotting of His6-ANXA2 or control proteins with antiserum against CKGGRAKDC or control preimmune serum, as indicated. Arrow: His6-ANXA2. (B) Binding of CKGGRAKDC-displaying phage is specifically inhibited by the synthetic peptide. Binding of unrelated control phage, insertless phage, binding to BSA and inhibition with an unrelated peptide served as controls. (C and D) Association of prohibitin and ANXA2 with membrane lipid rafts. Membrane proteins extracted from human WAT were subjected to immunoblotting or to fractionation enriching for noncaveolar or caveolar lipid rafts. Proteins recognized by anti-ANXA2 (C), antiprohibitin (D, upper box), and anticaveolin 1 antibodies (D, lower box) are indicated by arrows. (E) Binding of prohibitin and ANXA2 in vitro. Increasing concentrations of GST-prohibitin or GST control were captured with His6-ANXA2 or control His6-ANXA5. Specific binding was assessed with anti-GST antibodies. Arrow indicates GST-prohibitin (migrating as several bands). (F and G) Vascular expression of ANXA2 in human WAT. Immunohistochemistry with anti-ANXA2 and antiprohibitin antibodies on human WAT demonstrated colocalization of ANXA2 and prohibitin in the vasculature. Blood vessels identity was confirmed by staining with anti-VE-cadherin antibody (G, inset). Arrows point to blood vessels. Red insets show lower magnification of the corresponding area. (Scale bar, 100 μm).