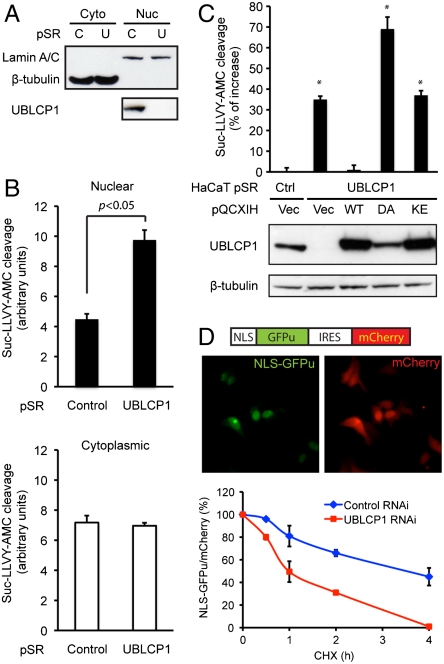
Fig. 4.
UBLCP1 knockdown enhances nuclear proteasome activity. (A) Cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractionation of ZR751 breast cancer cells stably expressing either control (C) or UBLCP1-specific (U) shRNA built in the pSuperRetro vector (pSR). Lamin A/C and β-tubulin were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively. (B) Proteasome activity assay using the same extracts as in A. Normalized AMC fluorescence is represented as the average ± SD. (C) UBLCP1 rescue experiments with HaCaT double-stable lines. UBLCP1 expression levels are determined by Western blotting. Nuclear proteasome activity was measured by in-well assays. Data are presented as the percent increase in activity versus control. *, p < 0.05. (D, Top) A schematic of the NLS-GFPu reporter in an IRES-mCherry backbone (26) and localization of the fluorescent proteins in 293T cells. (Bottom) GFPu/mCherry ratio during cycloheximide (CHX) treatment time course, with the starting value at time 0 being 100%. Data were analyzed from three independent experiments.