Figure 6.
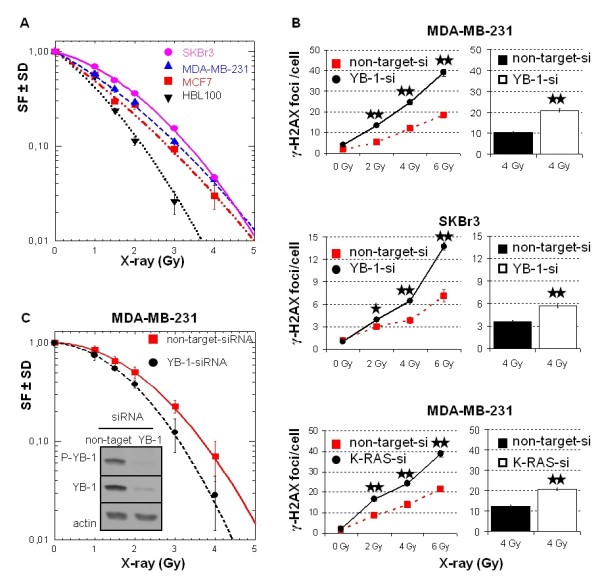
YB-1 regulates repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA-DSB and postirradiation survival. (A) Colony-forming assay was performed as described in Materials and methods. Preplated cells were irradiated with single doses of 1, 1.5, 2, 3 and 4 Gy. Ten days later cultures were stained, and colonies with more than 50 cells were counted. The surviving fraction (SF) of irradiated cells was normalized to the plating efficiency of nonirradiated controls. Data represent the average SF ± standard deviation (SD) of at least three biologically independent experiments, with each experiment containing six parallel data sets (N = 18). (B) Indicated cells were transfected with nontargeting small interfering RNA (siRNA) or siRNA against YB-1 and K-RAS. Three days after transfection cells were mock-irradiated or irradiated with 2, 4 or 6 Gy. After 24 hours, the γ-H2AX focus assay was performed. Using a fluorescence microscope, we counted the number of γ-H2AX foci in 70 to 250 nuclei for each individual condition and graphed them. Using Student's t-test, we found that YB-1 siRNA as well as K-RAS siRNA transfection resulted in significantly enhanced residual γ-H2AX foci (*P < 0.01 and **P ≤ 2.13 × 10-8). Bar histograms represent data for residual γ-H2AX foci observed in two independent experiments after irradiation of cells with 4 Gy. (C) Three days after transfecting MDA-MB-231 cells with indicated siRNA, cells were seeded into six-well plates for clonogenic assay. Twenty-four hours later cultures were irradiated with indicated doses of ionizing radiation and incubated at 37°C. Ten days later cultures were stained, and colonies with more than 50 cells were counted. The SF of irradiated cells was normalized to the plating efficiency of nonirradiated controls. Data represent the average SF ± SD of six parallel experiments. The significance of the effects YB-1 siRNA on postirradiation survival was assessed using Student's t-test. Except for the 1-Gy radiation dose (P = 0.089), the effects of YB-1 siRNA at the radiation doses of 1.5, 2, 3, and 4 Gy proved to be statistically significant at the following P values: P(1.5 Gy) = 0.006, P(2 Gy) = 0.003, P(3 Gy) = 0.001 and P(4 Gy) = 0.015. From the cultures used for clonogenic assay, protein samples were isolated and levels of P-YB-1, YB-1 and actin were detected using Western blot analysis.
