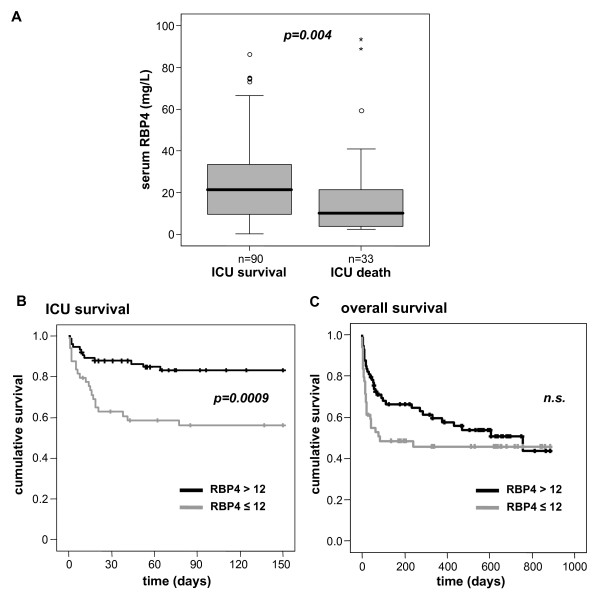
Figure 5.
Prognostic relevance of serum RBP4 in critically ill patients. (a) Patients who die during the course of ICU treatment have significantly (P = 0.004) lower serum RBP4 levels on admittance to ICU than survivors. Boxplots are displayed, where the black bold line indicates the median per group, the box represents 50% of the values, and horizontal lines show minimum and maximum values of the calculated nonoutlier values; asterisks and open circles indicate outlier values. (b) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of ICU patients (n = 123) are displayed, showing that patients with high RBP4 levels (> 12 mg/L, black) have a decreased short-term mortality at ICU as compared to patients with low RBP4 (< 12 mg/L, gray). P value from Cox regression analysis is given. (c) Kaplan-Meier survival curves of ICU patients show no difference with respect to the long-term survival between patients with RBP4 levels (> 12 mg/L, black) and patients with low RBP4 (< 12 mg/L, gray). n.s., not significant.