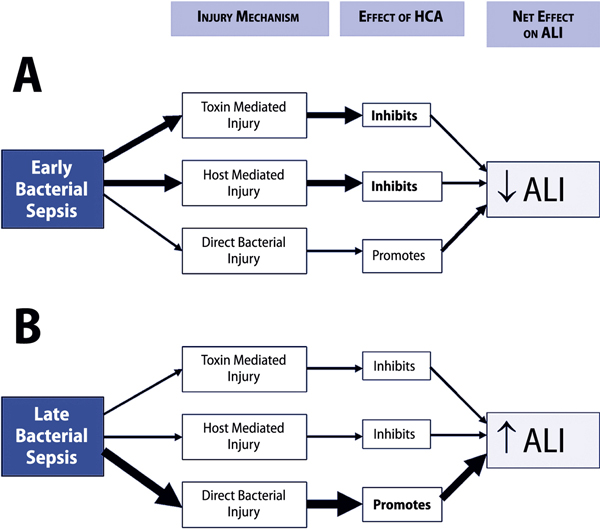
Figure 2.
Potential mechanisms underlying the effects of hypercapnic acidosis in sepsis. Panel A represents early sepsis, in which hypercapnic acidosis may reduce the host inflammatory response and decrease the contribution of bacterial toxin mediated injury to tissue injury and damage. This might result in an overall decrease in lung injury. Panel B represents late or prolonged bacterial sepsis, where a hypercapnic acidosis-mediated decrease in the host response to bacterial infection might result in unopposed bacterial proliferation, thereby increasing direct bacterial tissue invasion and injury, and worsening lung injury. ALI: acute lung injury; HCA: hypercapnic acidosis.