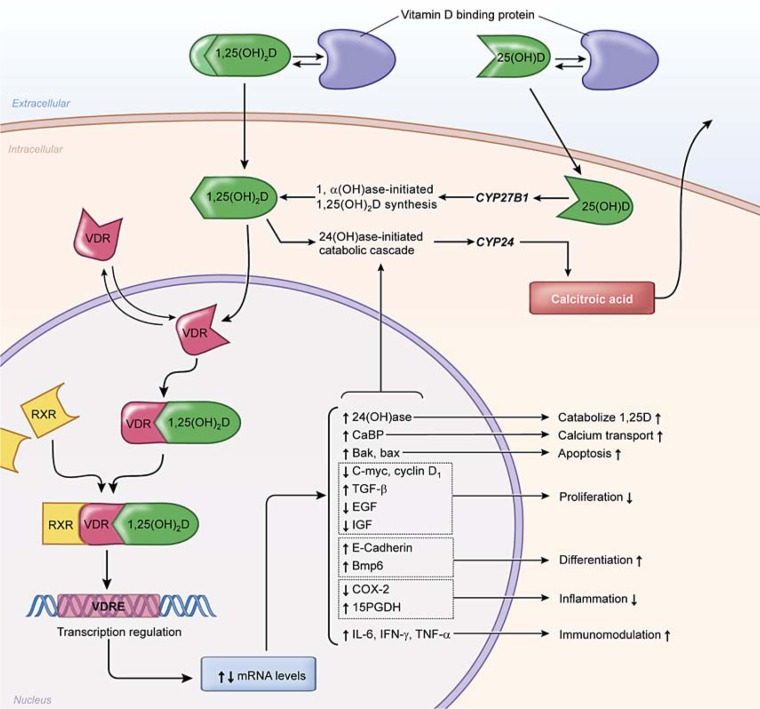
Fig. 1.
Proposed mechanism of action of 1,25(OH)2D in target cells. 1,25(OH)2D binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) and forms a heterodimer with the retinoid X receptor (RXR). This complex binds to the vitamin D response element (VDRE) to induce or repress expression of target genes. Examples of genes with VDREs related to carcinogenesis include those involved in regulating apoptosis, proliferation, differentiation, inflammation and immunomodulation. Modified from McCullough et al. [39].