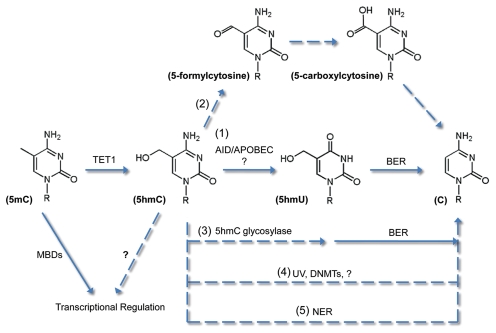
Figure 1.
Potential mechanisms for active DNA demethylation through 5hmC. (1) Evidence suggests that 5hmC may be converted to 5hmU by AID/APOBEC deaminases and repaired by the base excision repair (BER) pathway. (2) 5hmC may also be further oxidized to 5-carboxylcytosine and decarboxylated/repaired to C. (3) A 5hmC glycosylases may excise 5hmC and directly initiate BER. (4) Direct conversion from 5hmC to C may also occur. (5) Nuclear excision repair (NER) pathway may excise 5hmC-containing DNA strands. Besides promoting DNA demethylation, 5hmC may regulate transcription through unidentified 5hmC-binding proteins. Solid arrows indicate catalytic steps that are supported by experimental evidence, whereas dashed arrows indicate speculative processes.