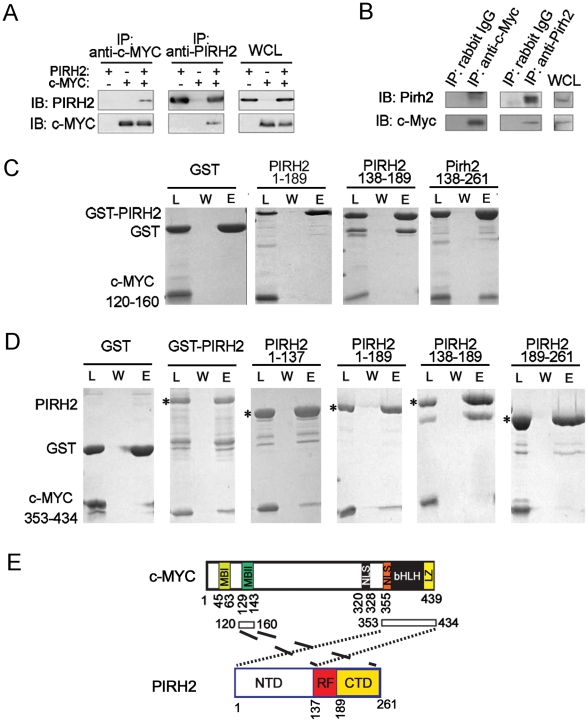
Figure 3. Characterization of the Interaction of PIRH2 and c-MYC.
(A) Interaction of human PIRH2 and c-MYC. HEK293T cells were transfected with expression plasmids encoding PIRH2 and c-MYC as indicated. Immunoprecipitation (IP) was performed with anti-PIRH2 or anti-c-MYC antibody and analyzed by immunoblot (IB). (B) NIH3T3 cells were lysed and IP performed with antibodies against murine Pirh2 or murine c-Myc, followed by IB analysis. A portion of the cell lysate corresponding to 3% of the input for IP was subjected to IB analysis. WCL: whole cell lysate. (C) PIRH2 interacts with the N-terminus of c-MYC. GST pull-down assays of GST-PIRH2 fusion proteins with c-MYCboxII (120–160 aa). Labeled lanes reflect loaded material (L), column flow-through after wash (W) and eluate (E). (D) GST pull-down assays of GST-PIRH2 with His-c-MYC (353–434 aa) protein. Star indicates GST-PIRH2 proteins. (E) Schematic representation of the interacting regions of PIRH2 and c-MYC. MBI: c-MYCboxI, MBII: MYCboxII, NLS: nuclear localization signal, bHLH: Basic region and Helix–loop–helix, LZ: leucine zipper.