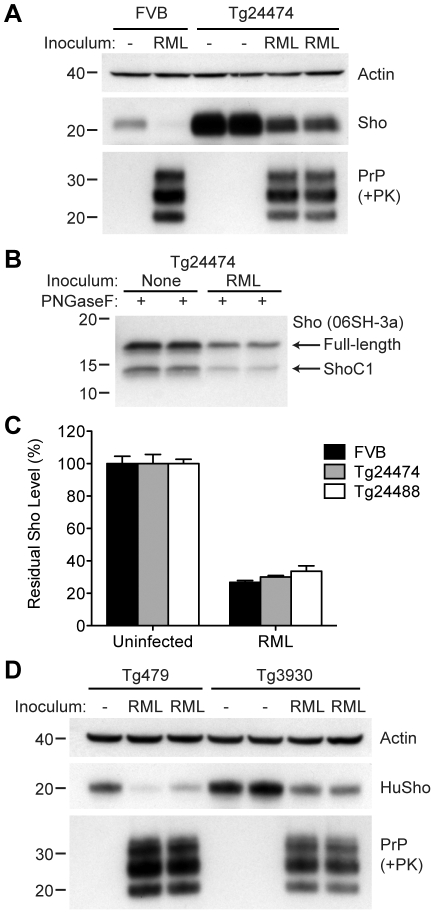
Figure 8. Sho levels in prion-infected Tg(MoSho) and Tg(HuSho) mice.
(A) Levels of Sho were decreased in RML prion-infected Tg(MoSho) mice compared to uninfected controls. For comparison, Sho and protease-resistant PrPSc levels in RML-infected, wt FVB mice are shown. The antibody HuM-P was used to probe PrP, and the antibody 06rSH-1 used to detect Sho. Actin levels are shown as a control. (B) RML prion infection resulted in decreased levels of both full-length and endoproteolytically trimmed Sho in Tg(MoSho) mice. All samples were treated with PNGaseF. The 06SH-3a antibody recognizing a C-terminal Sho epitope was used. (C) Quantification of Sho levels in wt and Tg(MoSho) mice (n = 3 for each group) following infection with RML prions. In all infected mice, Sho levels decreased by ∼70% compared to uninfected mice. (D) Levels of Sho were decreased in RML prion-infected Tg(HuSho) mice compared to uninfected controls. The antibody HuM-P was used to probe PrP, and the antibody S-12 used to detect Sho. Actin levels are shown as a control. For all Western blots, molecular masses based on the migration of protein standards are shown in kilodaltons.