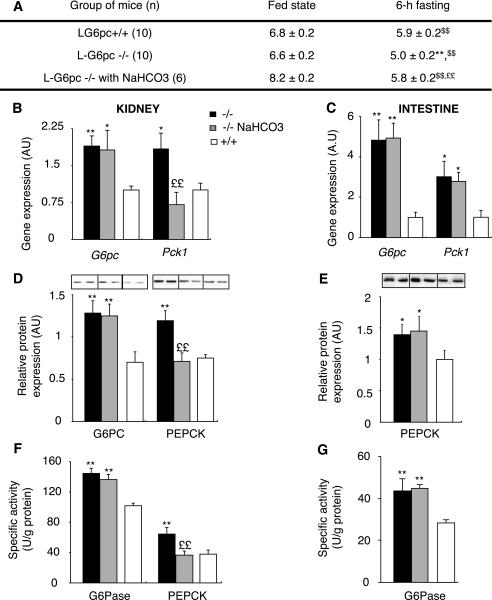
FIG. 7.
Renal gluconeogenesis of L-G6pc−/− mice is regulated by acidosis. A: Follow-up of urinary pH of L-G6pc−/− mice (black bars), L-G6pc−/− mice treated with 0.28 mol/L NaHCO3 in drinking water (gray bars), and WT (L-G6pc+/+ mice, white bars) on the fed or postabsorptive state. Values of pH were determined using strips with ΔpH = 0.2. B and C: Expression levels of mRNA encoding G6pc or Pck1 gene in the kidneys (B) or in the intestine (C) of 6 h–fasted mice. Results are expressed as a ratio relative to Rpl19 expression levels. D–G: Western blot quantification and enzyme activity assays of G6Pase and PEPCK determined in the kidneys (D and F) or in the intestine of 6 h–fasted mice (E and G). Data were obtained 5 weeks after gene deletion and are expressed as mean ± SEM. Values significantly different from WT (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01), from the fed state ($$P < 0.01), and from L-G6pc−/− without NaHCO3 treatment (££P < 0.01).