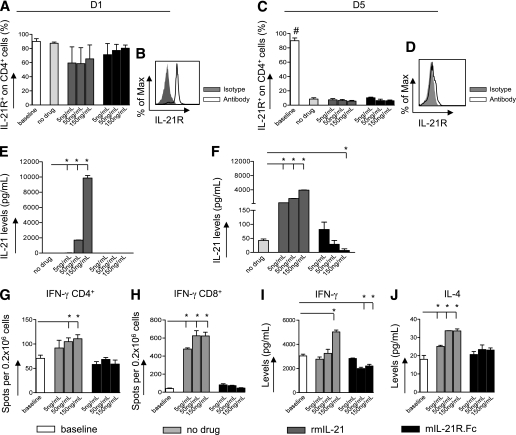
FIG. 1.
IL-21 is a cytokine of the late phase of the alloimmune response in vitro. The percentage of IL-21R+ CD4+ T cells (obtained from C57BL/6 mice) after 1 day (D1) (A and B) and 5 days (D5) (C and D) in an anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation assay in the presence of increasing concentrations of 5, 50, and 150 ng/mL rmIL-21 or mIL-21R.Fc or medium alone (no drug) (n = 3 experiments/conditions) was determined. IL-21R was highly expressed on CD4+ T cells, without any considerable changes after day 1 (A and B). At day 5, the percentage of IL-21R+CD4+ T cells was reduced compared with baseline in all conditions tested (baseline vs. all, #P < 0.05) (C and D). IL-21 levels in supernatants obtained in the anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation assay were evaluated using the Luminex assay at different time points (n = 3 experiments/conditions). No detectable levels of IL-21 were found in supernatants at day 1 after stimulation (E), whereas an increase was observed at day 5. High concentrations of mIL-21R.Fc (150 ng/mL) significantly reduced IL-21 levels (no drug vs. 150 ng/mL mIL-21R.Fc, *P = 0.01) (F). The addition of serial concentrations of rmIL-21 induced an increase in IL-21 levels at days 1 and 5 (no drug vs. rmIL-21, *P < 0.05) (E). IFN-γ–producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells extracted from naïve C57BL/6 mice and cultured with anti-CD3/CD28 in the presence of 5, 50, and 150 ng/mL rmIL-21 or mIL-21R.Fc or with medium alone (no drug) were evaluated using the ELISpot assay (G and H) (n = 3 experiments/conditions). An increase in IFN-γ–producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells was evident on the addition of rmIL-21 (no drug vs. 50 and 150 ng/mL rmIL-21, *P < 0.05) (G and H). The frequencies of IFN-γ–producing CD4+ and CD8+ T cells did not change when mIL-21R.Fc was added to the anti-CD3/CD28 assay (no drug vs. 5, 50, and 150 ng/mL mIL-21R.Fc, NS) (G and H). IFN-γ and IL-4 levels were evaluated in supernatants obtained from anti-CD3/CD28 stimulation assays at day 5 using the Luminex assay (n = 3 experiments/conditions). Increased levels of IFN-γ were detected in the presence of rmIL-21 (no drug vs. 150 ng/mL rmIL-21, *P = 0.0008), whereas IFN-γ levels were reduced in the presence of mIL-21R.Fc (no drug vs. 50 and 150 ng/mL mIL-21R.Fc, *P < 0.05) (I). A dose-dependent increase in IL-4 levels was observed in the presence of rmIL-21 (no drug vs. 5, 50, and 150 ng/mL rmIL-21, *P < 0.05), whereas no changes were evident in the presence of mIL-21R.Fc (no drug vs. 5, 50, and 150 ng/mL mIL-21R.Fc, NS) (J).