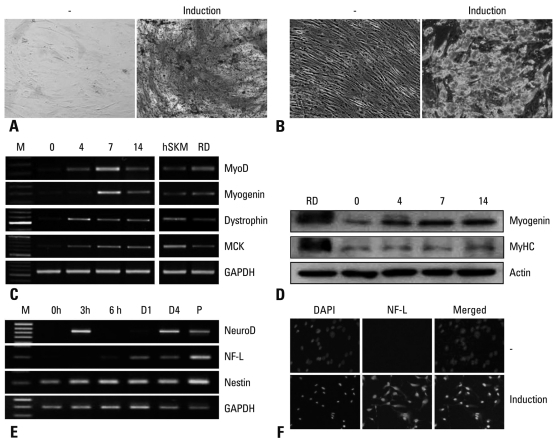
Fig. 4.
Differentiation potentials of ASCs isolated from lipoaspirates preserved for 24 hours. Passage 1 cells were seeded and differentiated into adipocytes, osteoblasts, muscle cells, or neuronal cells as described in the Materials and Methods section. Osteogenic (A) or adipogenic differentiation (B) were evaluated by assaying the alkaline phosphatase activity or Oil-Red O staining, respectively. To evaluate differentiation potentials of ASCs into muscle (C and D) or neuronal cells (E and F), we investigated the expression of several markers (myogenic; MyoD, Myogenin, Dystrophin, MCK and neurogenic; NeuroD, NF-L, Nestin) by RT-PCR, immunoblotting (myogenic; Myogenin and MyHC), and immucocytochemistry (neurogenic; NF-L). ASCs, adipose tissue-derived stem cells; MyoD, class I myosin; MCK, muscle creatine kinase; NeuroD, neurogenic differentiation; NF-L, neurofilament light polypeptide; DAPI, 4', 6-diamino-2-phenylindole; MyHC, myosin heavy chain.