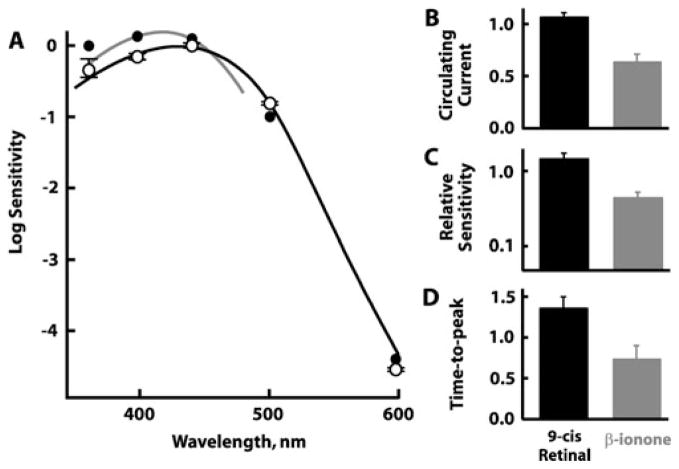
Fig. 3.
(A) Spectral sensitivities of seven dark-adapted BS rods after incubation with 12.7 ± 4.5 μM 9-cis retinal for 20 min. Results for six cells are presented as mean ±SEM (open circles), while the cell with the greatest shift in spectral sensitivity is presented separately (filled circles). For reference, curves are shown for BS rods with native chromophore (black line; Ma et al., 2001) or BS cones bleached and pretreated with 9-cis retinal (gray line; Makino et al., 1999). The latter curve was shifted vertically to overlay the results of the cell with the greatest sensitivity to short wavelengths. (B–D) Effects of 9-cis retinal on the circulating current (n = 5) (B), relative sensitivity (n = 5) (C), and response kinetics (n = 3) (D) normalized to dark-adapted preexposure values. On average, the circulating current, relative sensitivity to flashes, and dim flash response time to peak increased after treatment with 9-cis retinal (black bars), but all three parameters were reduced during subsequent perfusion with β-ionone (gray bars). Error bars represent SEM. SEM, standard error of mean.